Lesson 3
What Are Probabilities?
Problem 1
List the sample space for each chance experiment.
-
Flipping a coin
-
Selecting a random season of the year
-
Selecting a random day of the week
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 2
A computer randomly selects a letter from the alphabet.
- How many different outcomes are in the sample space?
- What is the probability the computer produces the first letter of your first name?
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 3
What is the probability of selecting a random month of the year and getting a month that starts with the letter “J?” If you get stuck, consider listing the sample space.
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 4
\(E\) represents an object’s weight on Earth and \(M\) represents that same object’s weight on the Moon. The equation \(M = \frac16E\) represents the relationship between these quantities.
- What does the \(\frac16\) represent in this situation?
-
Give an example of what a person might weigh on Earth and on the Moon.
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 2, Lesson 4.)Problem 5
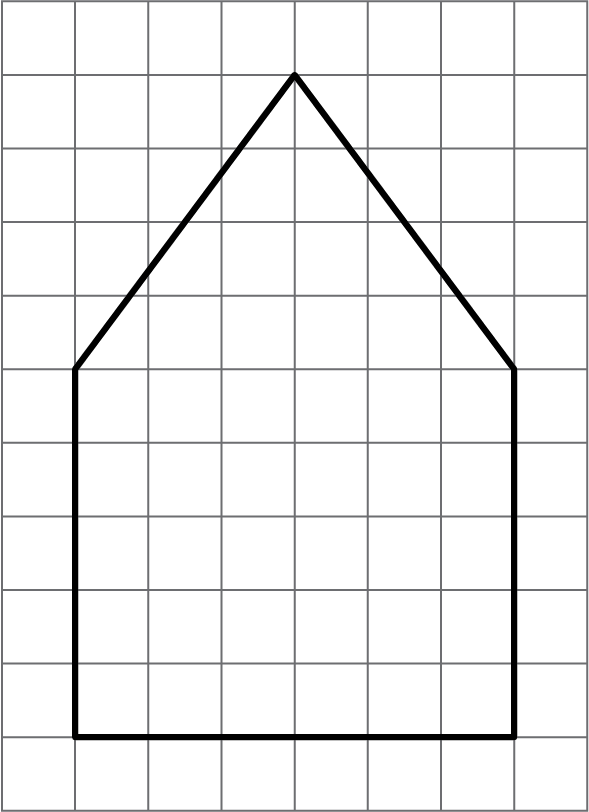
Here is a diagram of the base of a bird feeder which is in the shape of a pentagonal prism. Each small square on the grid is 1 square inch.
The distance between the two bases is 8 inches. What will be the volume of the completed bird feeder?
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 7, Lesson 13.)Problem 6
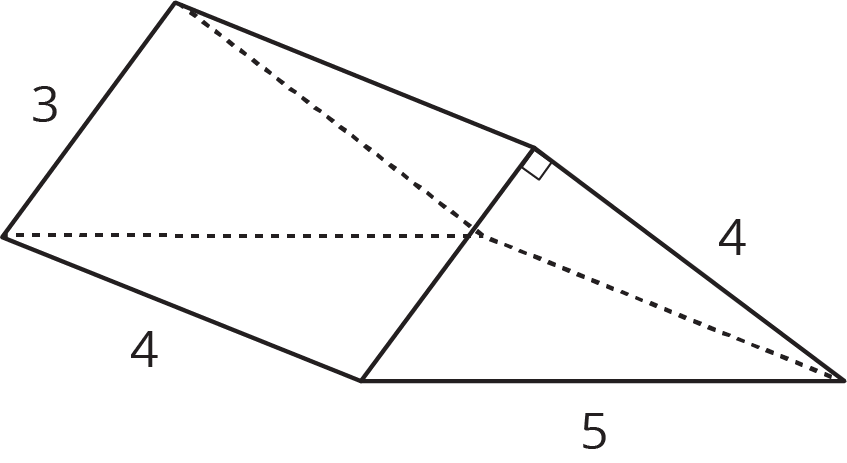
Find the surface area of the triangular prism.
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 7, Lesson 14.)