Lesson 11
More Solutions to Linear Equations
Problem 1
For each equation, find \(y\) when \(x=\text-3\). Then find \(x\) when \(y=2\)
- \(y=6x+8\)
- \(y=\frac23x\)
- \(y=\text-x+5\)
- \(y=\frac34x-2\frac12\)
- \(y=1.5x +11\)
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 2
True or false: The points \((6,13)\), \((21,33)\), and \((99,137)\) all lie on the same line. The equation of the line is \(y=\frac43x+5\). Explain or show your reasoning.
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 3
Here is a linear equation: \(y=\frac14 x +\frac54\)
- Are \((1,1.5)\) and \((12,4)\) solutions to the equation? Explain or show your reasoning.
- Find the \(x\)-intercept of the graph of the equation. Explain or show your reasoning.
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 4
Find the coordinates of \(B\), \(C\), and \(D\) given that \(AB\) = 5 and \(BC\) = 10.
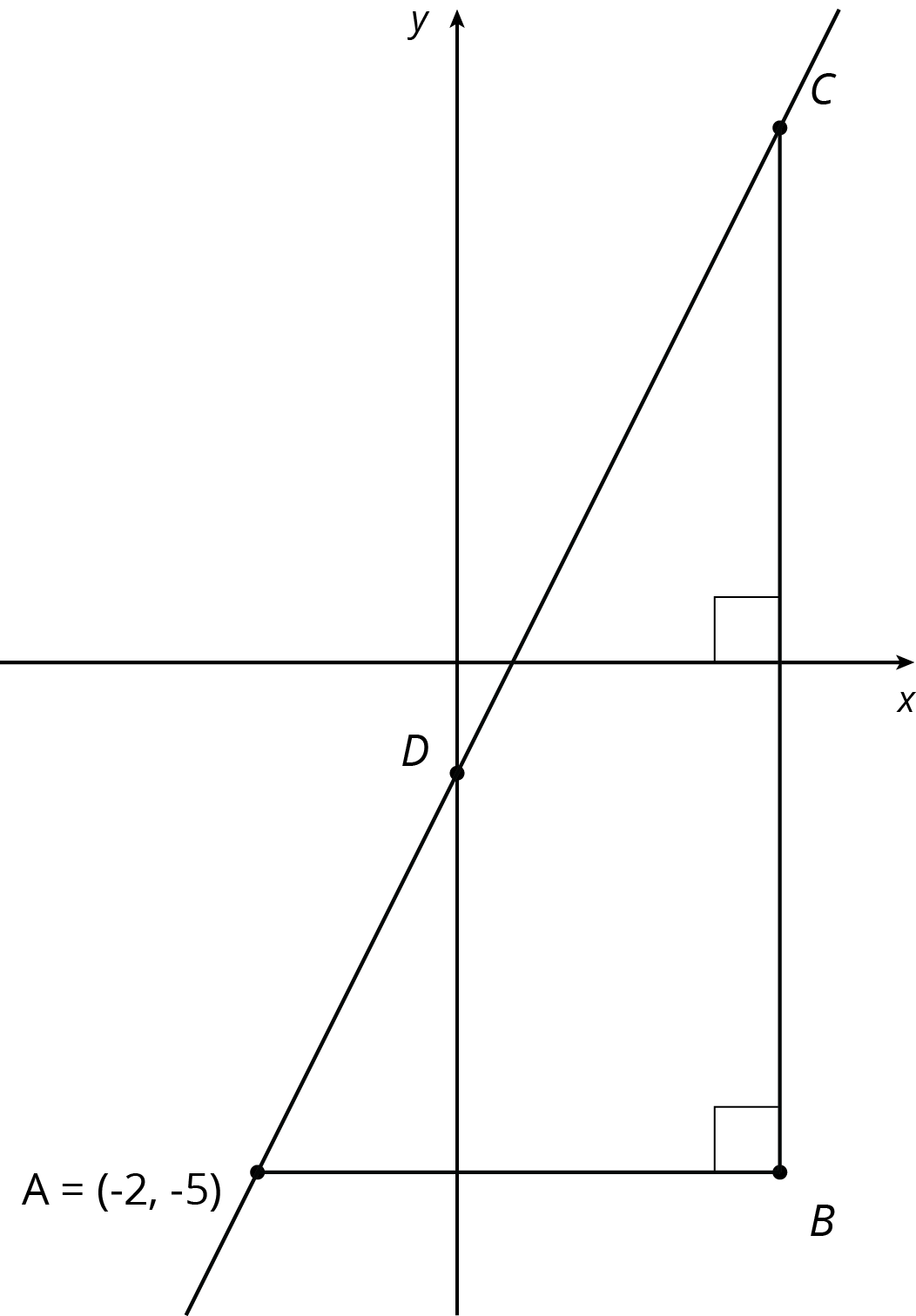
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 2, Lesson 16.)Problem 5
Match each graph of a linear relationship to a situation that most reasonably reflects its context.

Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 5, Lesson 8.)