Lesson 10
Meet Slope
10.1: Equal Quotients (5 minutes)
Warm-up
In this lesson, students will need to recognize equivalent fractions and decimals. This warm-up is designed to activate prior understanding.
Launch
Ask students if they can think of some different ways to write numbers that are equal to \(1 \div 2\). Some examples might be \(\frac48\) or 0.5. Tell them that in this warm-up, they will think of numbers that equal \(15 \div 12\). Give students 30–60 seconds to write as many as they can, or ask them to come up with at least three or four different numbers equal to \(15 \div 12\).
Student Facing
Write some numbers that are equal to \(15 \div 12\).
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Anticipated Misconceptions
Students may believe that this question must have only one acceptable response. To convince them that equivalent values are acceptable, you may need to appeal to the fact that one location on a number line can be expressed many different ways, depending on how you decide to subdivide a portion of the line.
Activity Synthesis
Ask students to share their strategies for finding numbers equal to \(15 \div 12\). Record and display their answers and strategies for all to see. To involve more students in the conversation, consider asking:
- “Who can restate ___’s reasoning in a different way?”
- “Did anyone solve the problem the same way but would explain it differently?”
- “Did anyone solve the problem in a different way?”
- “Does anyone want to add on to _____’s strategy?”
- “Do you agree or disagree? Why?”
10.2: Similar Triangles on the Same Line (20 minutes)
Activity
In this activity, students explain why certain triangles with one side along the same line are similar. This fact about the triangles will be used to define the slope of the line. Students may show that the triangles are similar by describing a sequence of transformations and dilations or by AA (or AAA). Alternatively, they may use the fact that grid lines are parallel and use what they know about the angles where a transverse meets a pair of parallel lines.
Monitor for students who use different methods for showing that the triangles are similar. Look for these methods in particular:
- Describing a sequence of transformations
- AA (or AAA) arguments using what students know about angles made by parallel lines with a transversal
Students need to use the structure of the grid for either argument (MP7). For the similarity argument, they need to use the grid to describe transformations and dilations. For the AA argument, they need to use the fact that vertical or horizontal grid lines are parallel. In both cases, constructing a viable argument (MP3) will require care and focus.
Launch
Before starting the activity, if possible, display this link https://ggbm.at/UxvbFxVQ for all students to see. Tell students that the goal is to make one triangle match up with the other triangle. Demonstrate how the controls work. Then, invite students to describe how you should manipulate the controls to make the triangles match up. Remind students to use words associated with transformations like translate and scale factor.
Arrange students in groups of 2. Assign one partner triangles \(ABC\) and \(CDE\) and the other partner \(ABC\) and \(FGH\). Give students 5 minutes of quiet time to construct an argument for why their two triangles are similar. Remind students that if they claim something is true, they should explain how they can be sure it is true.
After a few minutes of quiet work time, ask students to share their reasoning with their partner and listen to their partner’s explanation for why their triangles are similar. Then tell them to work with their partner to finish the activity.
Supports accessibility for: Language; Organization
Design Principle(s): Cultivate conversation; Support sense-making, Meta-awareness of the language
Student Facing
-
The figure shows three right triangles, each with its longest side on the same line. Your teacher will assign you two triangles. Explain why the two triangles are similar.
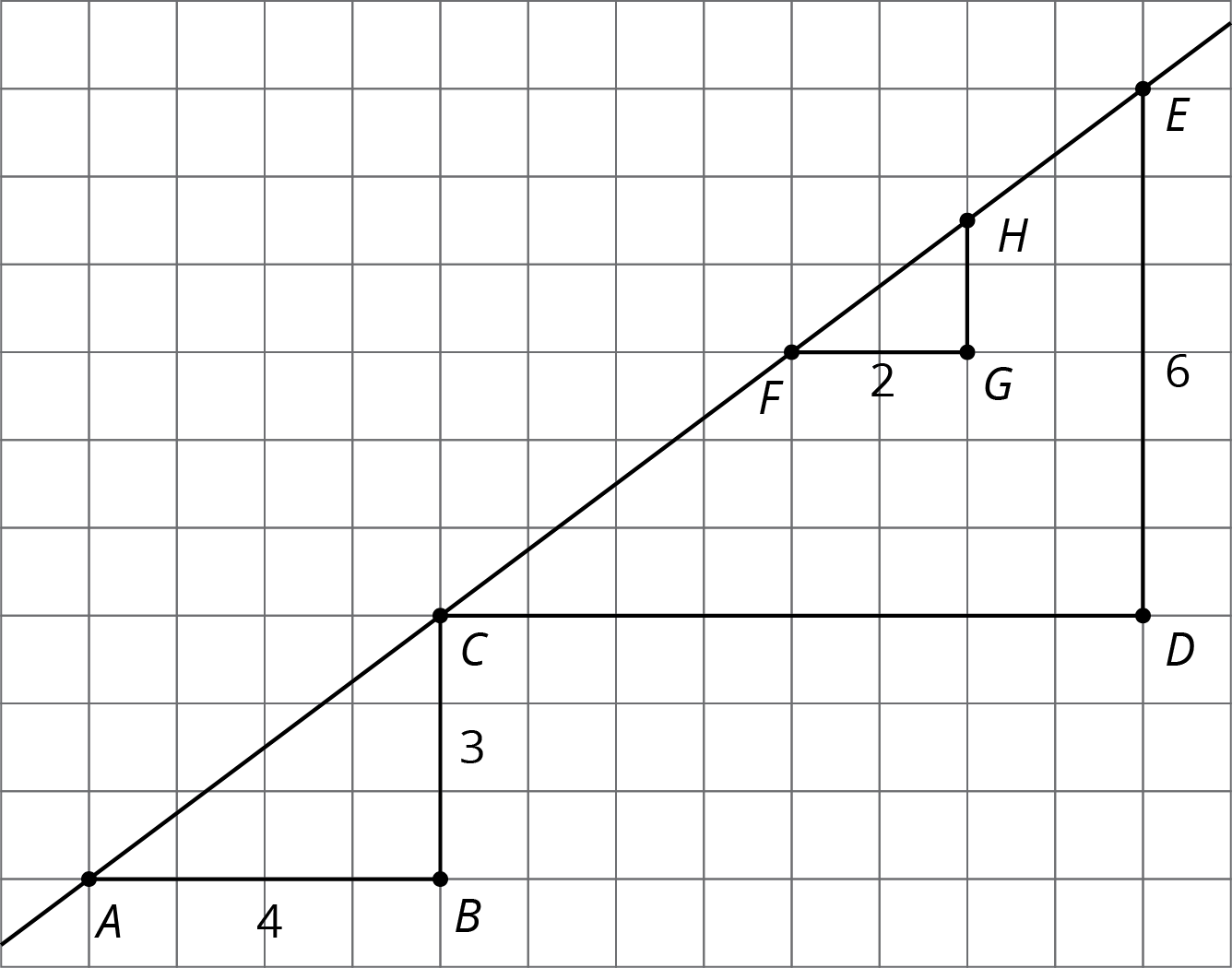

- Complete the table.
triangle length of
vertical sidelength of
horizontal side(vertical side) \(\div\) (horizontal side) \(ABC\) \(CDE\) \(FGH\)
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Anticipated Misconceptions
If students struggle getting started, ask them what it means for two triangles to be similar (there is a sequence of translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations taking one to the other).
Activity Synthesis
Invite selected students to share their methods for showing that the triangles are similar. Sequence them so that a similarity transformation argument goes first, followed by an AA (or AAA) argument. For these particular triangles, describing a sequence of transformations is quick and efficient: a translation and dilation (or a dilation followed by a translation) naturally present themselves for these triangles. The AA argument requires a little extra work because no angle measures are labeled: finding angle measures uses the structure of the grid and previous results about corresponding angles created by parallel lines and a transversal. Make sure students understand that since triangles \(ABC\) and \(FGH\) are each similar to triangle \(CDE\), they are similar to each other.
Relate the work on finding the quotients, in the second problem, back to the work in the last lesson looking at internal ratios of corresponding sides of similar triangles. Explain that whenever we have a (non vertical, non horizontal) line, we can construct triangles like these where one side is horizontal and one side is vertical, and the quotient of the length of the vertical side and the horizontal side will always be the same. This number is called the slope of the line. The slope of the line in this activity can be written as 0.75 or \(\frac34\) (or any value equal to these).
Make clear to students that the mathematical convention is to define slope using vertical length divided by horizontal length and not the other way around. Display the diagram below, or create a similar diagram with the same information. Post this diagram for reference for several days, well into the next unit of study, along with accompanying text:
The slope is \(\text{vertical length} \div \text{horizontal length}\). The slope of line \(\ell\) can be written as \(\frac68\), \(\frac34\), 0.75, or any equal value.
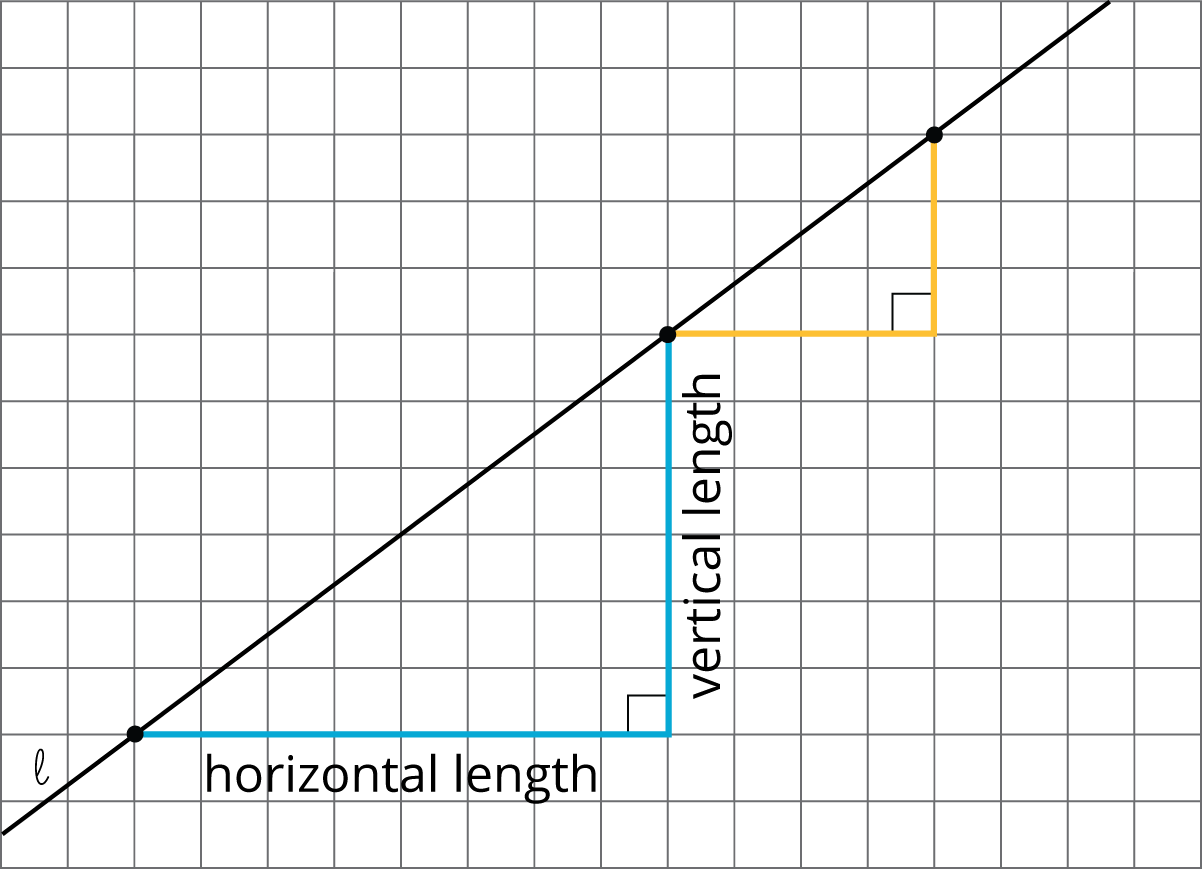
10.3: Multiple Lines with the Same Slope (10 minutes)
Activity
The previous activity introduces the slope of a line. In this activity, students practice graphing lines with a given slope. They observe two important properties of slope:
- Lines with the same slope are parallel.
- As the slope of a line increases so does its steepness (from left to right).
Look for students who draw slope triangles to help construct their lines. Other students may count off horizontal and vertical distances. Select students using each method to share during the discussion. Also watch for students who notice the facts listed above about parallel lines and the impact of the slope on the steepness of the line.
Launch
Tell students that they are going to apply the new idea of slope introduced in the previous activity as they draw and study properties of some lines with different slopes.
If using the print version of the materials, distribute straightedges. If using the digital version, students have access to a digital tool to draw lines.
Student Facing
- Draw two lines with slope 3. What do you notice about the two lines?
- Draw two lines with slope \(\frac{1}{2}\). What do you notice about the two lines?
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Launch
Tell students that they are going to apply the new idea of slope introduced in the previous activity as they draw and study properties of some lines with different slopes.
If using the print version of the materials, distribute straightedges. If using the digital version, students have access to a digital tool to draw lines.
Student Facing
- Draw two lines with slope 3. What do you notice about the two lines?
- Draw two lines with slope \(\frac{1}{2}\). What do you notice about the two lines?
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Student Facing
Are you ready for more?
As we learn more about lines, we will occasionally have to consider perfectly vertical lines as a special case and treat them differently. Think about applying what you have learned in the last couple of activities to the case of vertical lines. What is the same? What is different?
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Activity Synthesis
Ask selected students to share how they found their lines with slope 3. Sequence them so that students who use slope triangles present their work first and students who count horizontal and vertical displacement (without drawing a triangle) present second. Help students see that the second method is the same as the first except that the slope triangle connecting two points on the line is only “imagined” rather than drawn. Further, that it doesn’t matter if you go up 3 and over 1, or up 6 and over 2, or up 9 and over 3 . . . you get a line with the same slope. Encourage students to draw slope triangles if it helps them to see and understand the underlying structure.
If it does not come up during student comments, make sure that students notice that the two lines of slope 3 are parallel and so are the two lines with slope \(\frac{1}{2}\).
Also, point out that the lines of slope 3 are “steeper” than the lines of slope \(\frac{1}{2}\). Hence the definition of slope corresponds to our intuition in the sense that a larger slope corresponds to a “steeper graph” (going from left to right).
It is likely that some students will draw lines with slope -3 and \(\text-\frac12\). Display these alongside lines of slope 3 or slope \(\frac12\), and ask students to describe how they are alike and different. It is okay to let them know that the “uphill” lines (leaning to the right) are positive and “downhill” (leaning to the left) are negative. But you might also leave the question open, for now, about whether such lines have the same or different slopes, and how the slope would be different. Later lessons will focus on distinguishing positive from negative slopes.
Supports accessibility for: Attention; Social-emotional skills
Design Principle(s): Optimize output (for explanation)
10.4: Different Slopes of Different Lines (15 minutes)
Optional activity
Earlier in this lesson, students have seen that the slope of a line can be calculated using any (slope) right triangle, that is a right triangle whose longest side is on the line and whose other two sides are horizontal and vertical. In this activity, students identify given lines with different slopes and draw a line with a particular slope.
For lines D and E as well as the line that students draw, encourage students to draw in slope triangles to help calculate the slope. Monitor for students who draw slope triangles of different sizes and invite them to share during the discussion to reinforce the fundamental idea for this lesson: different slope triangles whose longest side lies on the same line give the same value for slope.
Launch
Instruct students to work individually to match each slope to a line and draw the line for the slope that does not have a match. Remind students of the previous definition of slope, referring to the display as necessary. Students still need a straightedge for drawing line F.
Supports accessibility for: Conceptual processing; Language
Student Facing
Here are several lines.
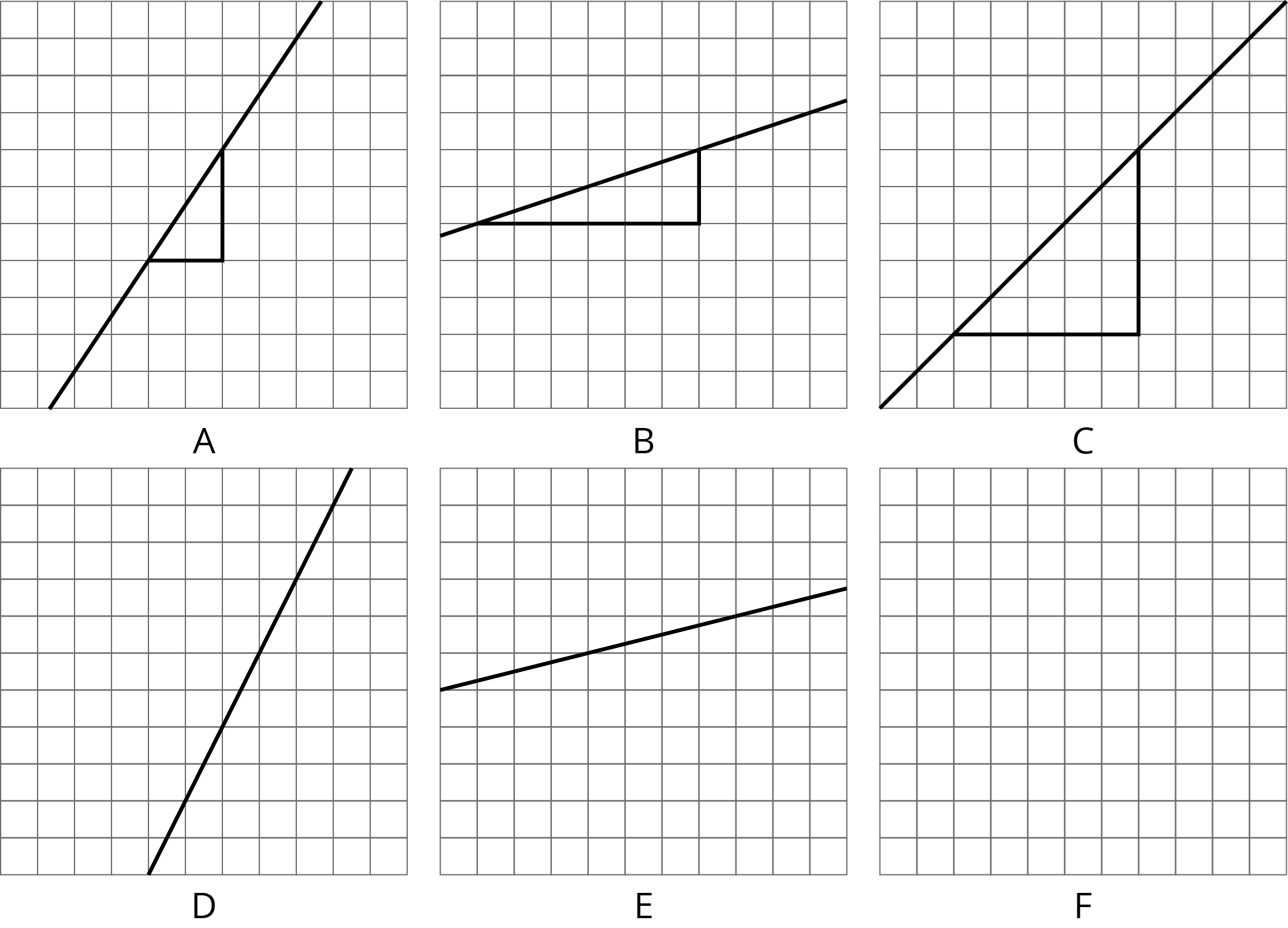

- Match each line shown with a slope from this list: \(\frac13\), 2, 1, 0.25, \(\frac32\), \(\frac12\).
- One of the given slopes does not have a line to match. Draw a line with this slope on the empty grid (F).
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Anticipated Misconceptions
For students who find it difficult to draw a triangle when one is not given, suggest that they examine two places on the line where the line crosses an intersection of grid lines.
Activity Synthesis
Two important conclusions for students to understand are:
- Given a line on a grid, they can draw a right triangle whose longest side is on the line, and then use the quotient of the vertical and horizontal sides to find the slope.
- Given a slope, they can draw a right triangle using vertical and horizontal lengths corresponding to the slope, and then extend the longest side of the right triangle to create a line with that slope.
When discussing line F, ask students to share how they drew their triangle. If possible, select students who drew their triangles correctly but at a different scale (for example, one student who used a triangle with a vertical length of 1 and a horizontal length of 2, and a different student who used a vertical length of 4 and a horizontal length of 8). Demonstrate (or get students who have drawn different triangles to do so) that the quotient of side lengths is the important feature, since any triangle drawn to match a given slope will be similar to any other triangle drawn to match the same slope.
Design Principle(s): Support Sense-making; Maximize meta-awareness
Lesson Synthesis
Lesson Synthesis
In this lesson, we learned what the slope of a line is. Discuss:
- “What is a slope triangle for a line?” (A triangle whose long side is on the line and whose other sides are horizontal and vertical.)
- “How can you use a slope triangle to find the slope of a line?” (Divide the length of the vertical side by the length of the horizontal side.)
- “Does it matter which two points you use to create a slope triangle? Why?” (No. Any two slope triangles are similar. So the quotient of the two corresponding sides will give the same value.)
- “Why are any two slope triangles similar?” (They are right triangles whose other angles are corresponding angles for a transverse meeting parallel grid lines.)
Consider creating a permanent classroom display showing the definition of slope.
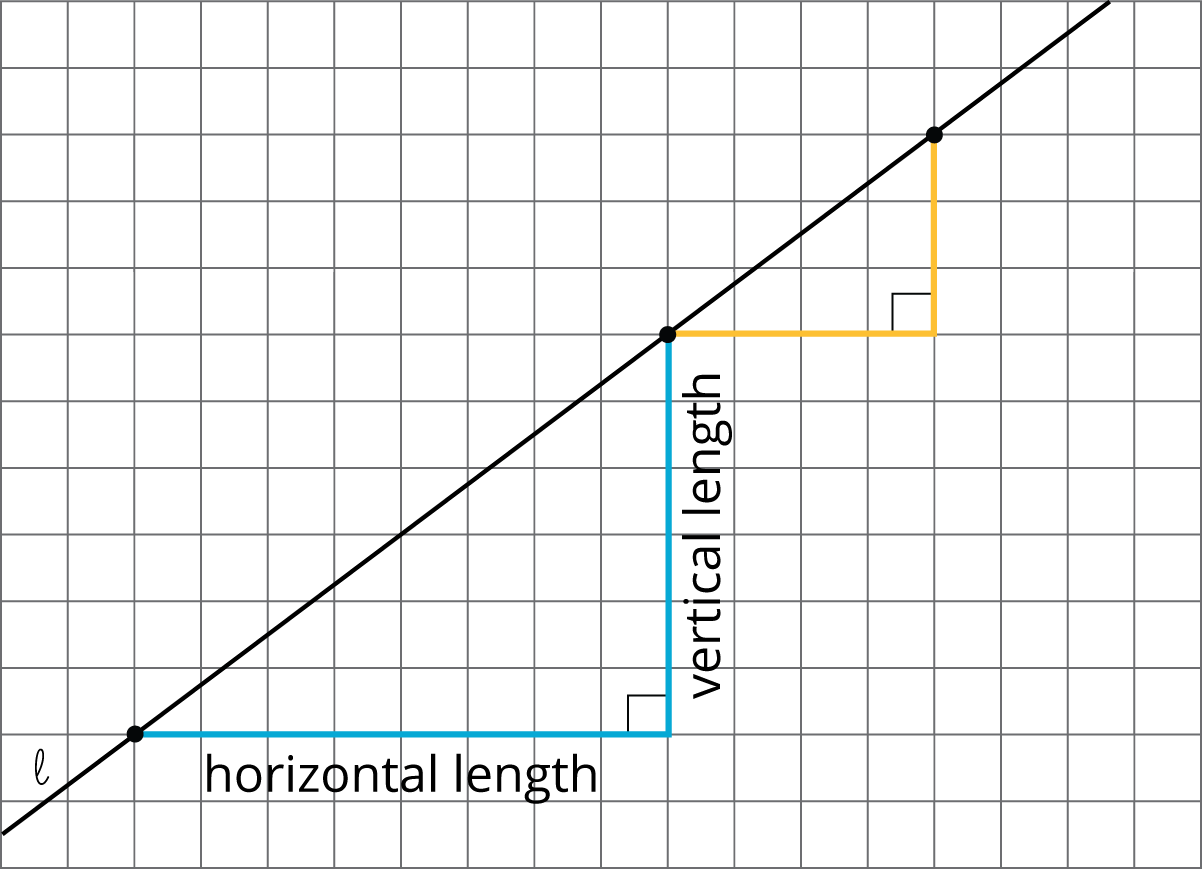
Display the diagram along with the accompanying text: The slope of the line is \(\text{vertical length} \div \text{horizontal length}\). The slope of line \(\ell\) can be written \(\frac68\), \(\frac34\), 0.75, or any equivalent value.
10.5: Cool-down - Finding Slope and Graphing Lines (5 minutes)
Cool-Down
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Student Lesson Summary
Student Facing
Here is a line drawn on a grid. There are also four right triangles drawn. Do you notice anything the triangles have in common?
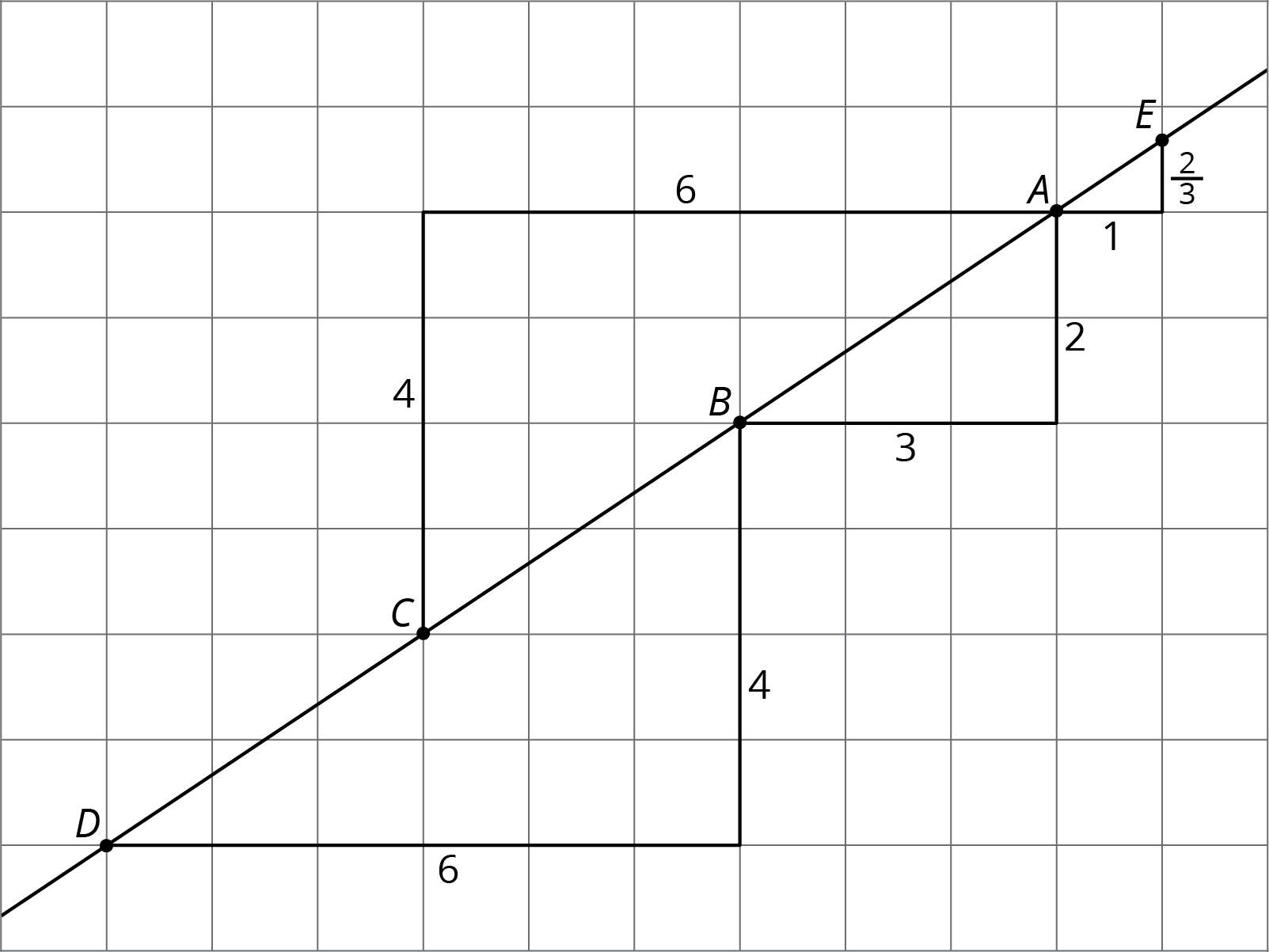

These four triangles are all examples of slope triangles. One side of a slope triangle is on the line, one side is vertical, and another side is horizontal. The slope of the line is the quotient of the length of the vertical side and the length of the horizontal side of the slope triangle. This number is the same for all slope triangles for the same line because all slope triangles for the same line are similar.
In this example, the slope of the line is \(\frac{2}{3}\), which is what all four triangles have in common. Here is how the slope is calculated using the slope triangles:
- Points \(A\) and \(B\) give \(2\div 3=\frac23\)
- Points \(D\) and \(B\) give \(4\div 6=\frac23\)
- Points \(A\) and \(C\) give \(4\div 6=\frac23\)
- Points \(A\) and \(E\) give \(\frac23 \div 1=\frac23\)