Lesson 4
Reasoning about Equations and Tape Diagrams (Part 1)
Problem 1
Draw a square with side length 7 cm.
- Predict the perimeter and the length of the diagonal of the square.
- Measure the perimeter and the length of the diagonal of the square.
- Describe how close the predictions and measurements are.
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 3, Lesson 1.)Problem 2
Find the products.
- \((100) \boldcdot (\text-0.09)\)
- \((\text-7) \boldcdot (\text- 1.1)\)
- \((\text-7.3) \boldcdot (5)\)
- \((\text-0.2) \boldcdot (\text-0.3)\)
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 5, Lesson 9.)Problem 3
Here are three stories:
-
A family buys 6 tickets to a show. They also pay a \$3 parking fee. They spend \$27 to see the show.
-
Diego has 27 ounces of juice. He pours equal amounts for each of his 3 friends and has 6 ounces left for himself.
-
Jada works for 6 hours preparing for the art fair. She spends 3 hours on a sculpture and then paints 27 picture frames.
Here are three equations:
- \(3x+6=27\)
- \(6x+3=27\)
- \(27x+3=6\)
- Decide which equation represents each story. What does \(x\) represent in each equation?
- Find the solution to each equation. Explain or show your reasoning.
- What does each solution tell you about its situation?
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 4
Here is a diagram and its corresponding equation. Find the solution to the equation and explain your reasoning.
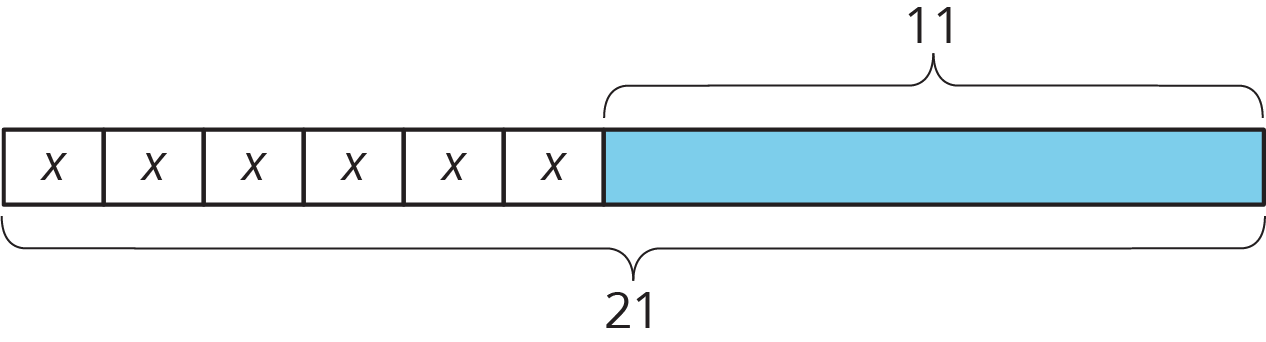
\(6x+11=21\)
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Problem 5
- Plot these points on the coordinate plane:
\(A= (3, 2), B= (7.5, 2), C= (7.5, \text-2.5), D= (3, \text-2)\)
- What is the vertical difference between \(D\) and \(A\)?
- Write an expression that represents the vertical distance between \(B\) and \(C\).
Solution
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
(From Unit 5, Lesson 7.)