Lesson 16
Round Numbers
Warm-up: Number Talk: Missing Numbers (10 minutes)
Narrative
This Number Talk encourages students to think about the distance of a number to a multiple of 100, 1,000, and 10,000 by relying on the structure of numbers in base-ten to mentally find differences (MP7). The understandings elicited here will be helpful later in the lesson when students round multi-digit whole numbers. It may be helpful to record students' reasoning on number lines.
Launch
- Display one equation.
- “Give me a signal when you have an answer and can explain how you got it.”
- 1 minute: quiet think time
Activity
- Record answers and strategy.
- Keep equations and work displayed.
- Repeat with each equation.
Student Facing
Find the value that makes each equation true mentally.
- \(421 + \underline{\hspace{1in}} = 500\)
- \(421 + \underline{\hspace{1in}} = 1,\!000\)
- \(6,\!421 + \underline{\hspace{1in}} = 7,\!000\)
- \(6,\!421 + \underline{\hspace{1in}} = 10,\!000\)
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Activity Synthesis
- “What do all four equations have in common?” (They are about finding how far away a number is to a multiple of 100, 1,000, or 10,000. The number on the left side of the equation is 421 or ends with 421.)
- “Is 500 the nearest multiple of 100 for 421? How do you know?” (No, 421 is closer to 400. It is 21 away from 400 and 79 from 500.)
- “Is 7,000 the nearest multiple of 1,000 for 6,421?” (No, 6,421 is closer to 6,000.)
- “Is 10,000 the nearest multiple of 10,000 for 6,421?” (Yes, 10,000 is less than 5,000 away from 6,421.)
Activity 1: Round to What? (20 minutes)
Narrative
Launch
- Groups of 2
- “What do you know about rounding?”
- 1 minute: quiet think time
- Share and record responses.
- Highlight responses that share times when students need to round numbers in their life.
- “What is 112 rounded to the nearest 10?” (110) “To the nearest 100?” (100)
- “Let’s round some larger numbers.”
Activity
- “Work with your partner to complete the activity.”
- 10 minutes: partner work time
- Monitor for students who consider all numbers that could be rounded to 490,000, to 500,000, and to both by:
- drawing a number line
- reasoning numerically
Student Facing
Noah says that 489,231 can be rounded to 500,000.
Priya says that it can be rounded to 490,000.
-
Explain or show why both Noah and Priya are correct. Use a number line if it helps.
- Describe all the numbers that round to 500,000 when rounded to the nearest hundred-thousand.
- Describe all the numbers that round to 490,000 when rounded to the nearest ten-thousand.
-
Name two other numbers that can also be rounded to both 500,000 and 490,000.
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Advancing Student Thinking
Students may be able to list some numbers that can be rounded to 500,000 (or 490,000) but may be unsure how to describe all of them. Encourage them to consider the upper and lower limits of the possible numbers by asking:
- “Which numbers cannot be rounded to 500,000 because they are too low?”
- “Which numbers cannot be rounded to 500,000 because they are too high?”
Activity Synthesis
- Display the number line from the activity.
- Select students to share their responses and reasoning for the first three problems. Record their responses.
- If no students mentioned using number lines to help them identify all the possible numbers that round to 500,000 and 490,000, ask them to try showing the ranges on the number line.
- Display students’ annotated number lines or the following:
- “How did you find numbers that can be rounded to both 500,000 and 490,000?” (I chose numbers that are between 485,000 and 494,999, since all of them can be rounded to 500,000. Numbers outside of that interval cannot be rounded to 490,000.)
Activity 2: Some Numbers to Round (15 minutes)
Narrative
In this activity, students round numbers to various place values. Here they encounter for the first time a number that rounds to 1,000,000 and some that round to 0. (For example, 4,896, rounded to the nearest 100,000 is 0.) Students may wonder why we might round a number in the thousands to the nearest 100,000. Make note of such ideas to discuss in the next lesson where students explore rounding in context and see that it often involves giving meaningful information.
Advances: Reading, Representing
Supports accessibility for: Conceptual Processing, Organization, Fine Motor Skills
Launch
- Groups of 2
- Display the table.
- “With your partner, choose at least three numbers—one with four digits, one with five digits, and one with six digits. Round them to the nearest values in the table.”
Activity
- “Work with your partner on the first two numbers and independently on at least one of them. Be prepared to explain or show your thinking.”
- 6–8 minutes: partner work
Student Facing
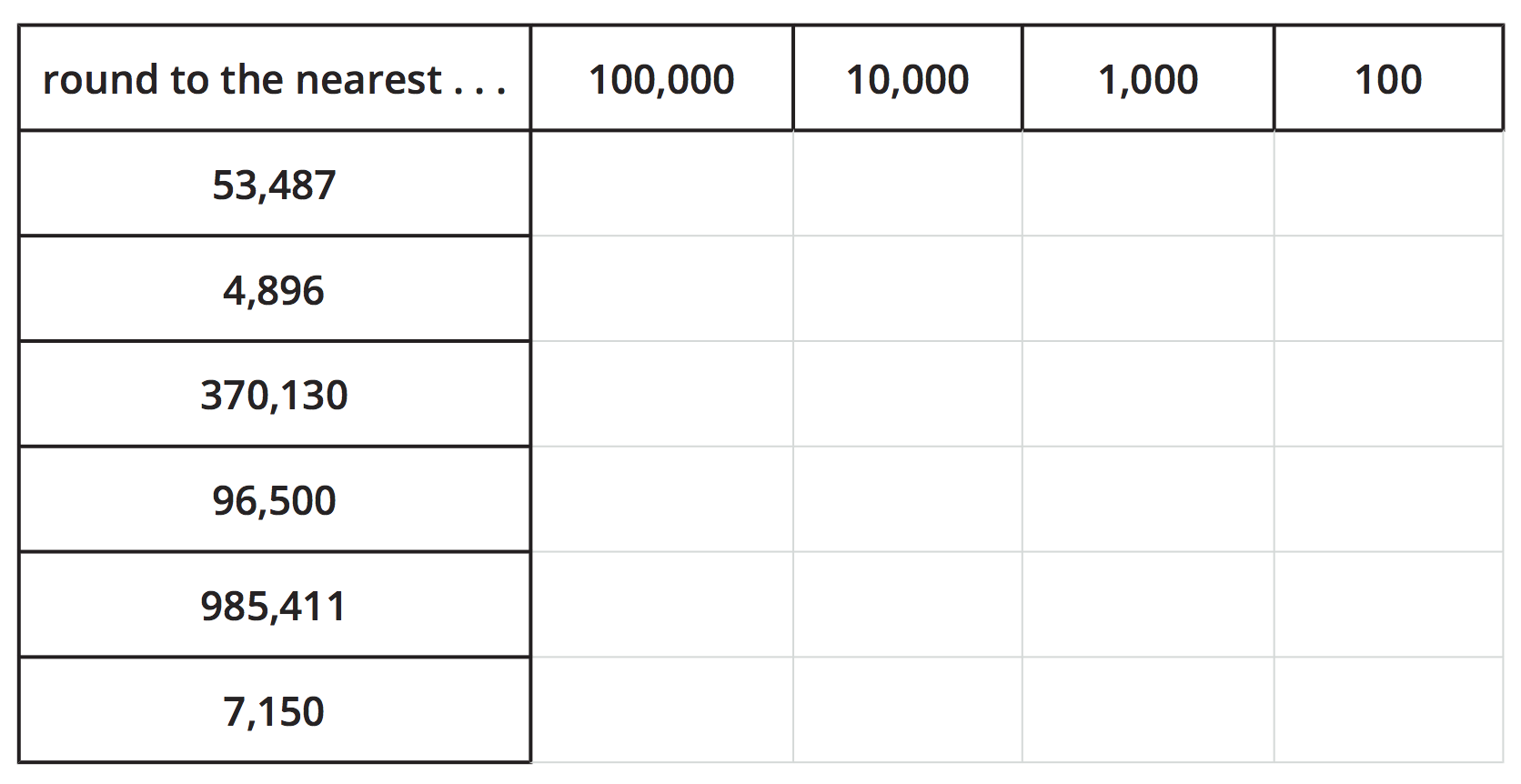
Your teacher will show you six numbers. Choose at least three numbers and round each to the nearest 100,000, 10,000, 1,000, and 100.
Record your work in the table. Use a number line if it is helpful.
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Activity Synthesis
- Display the blank table from the activity. Invite students to share their responses to complete the table. Discuss any disagreements.
- “The number 96,500 is the same distance from 96,000 and 97,000. How do we know which way to go if rounding to the nearest thousand?” (By convention, we round up.)
Activity 3: Rounded Populations [OPTIONAL] (20 minutes)
Narrative
Launch
- Groups of 2–4
- Display this table:

- “What do you notice? What do you wonder?”
- 1 minute: quiet think time
- Share responses.
- “When might it be helpful to have the actual population? When might it be helpful to have the rounded numbers?” (Sample responses:
- Rounding to the nearest million doesn’t quite make sense. It portrays the population either as 0—for Oakland—or as almost twice as large—for Mesa.)
- Counting every single person may not be possible.
- Rounding to the nearest 100,000 or 10,000 seems appropriate.)
- “Let’s round some other populations and see if we still think the same way.”
Activity
- “Match the populations of Charlotte, Jacksonville, and Virginia Beach to the rounded numbers in the table. Then, complete the table.”
- “Work with your group to complete the activity. Be prepared to explain how you make your matches.”
- 6–8 minutes: group work time
- Monitor for the ways students reason about the given populations and the rounded numbers.
Student Facing
The table shows the estimated populations of two cities in the United States, based on surveys in 2018.
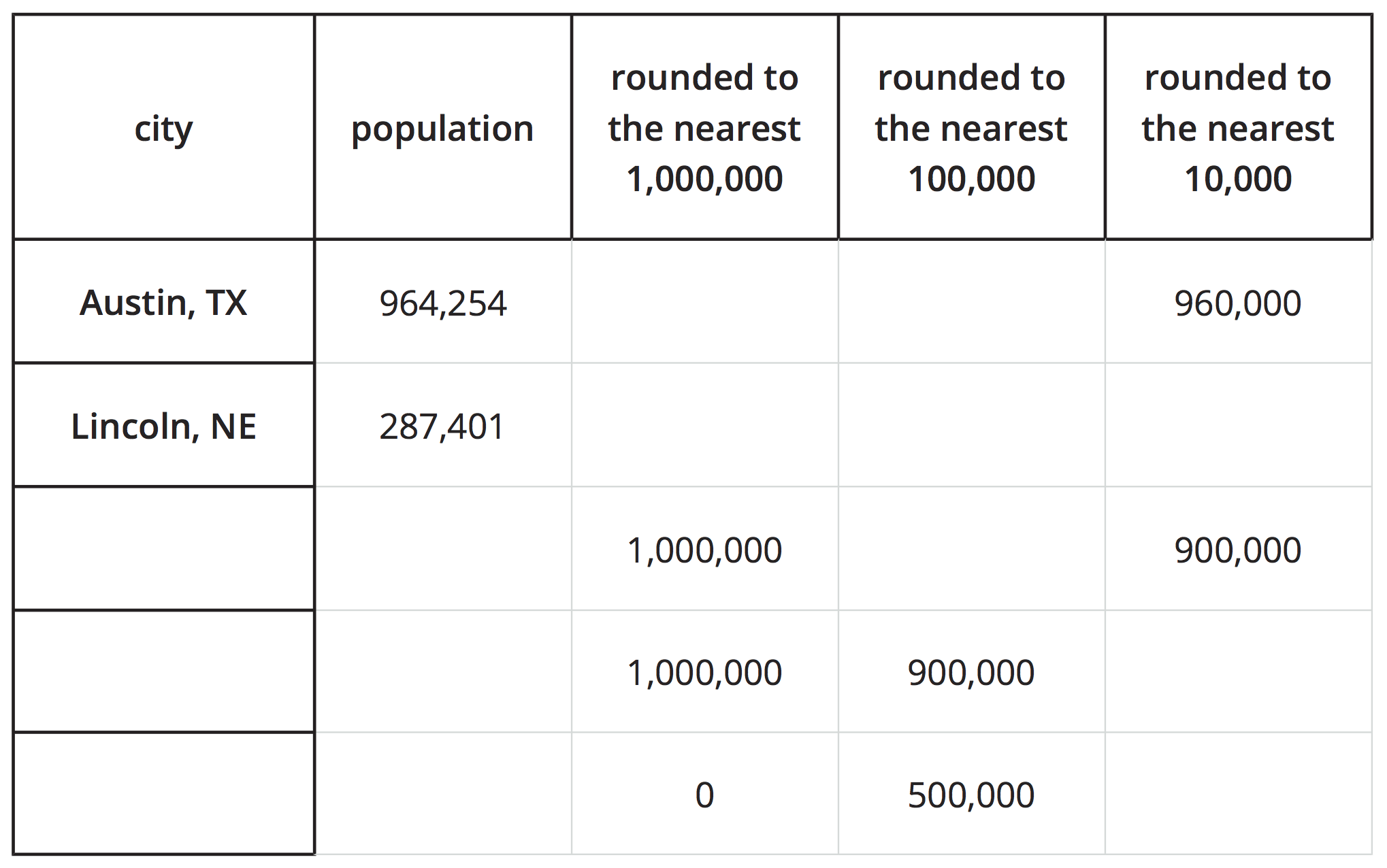
Here are three other cities and their estimated populations:
- Charlotte, NC: 872,498
- Jacksonville, FL: 903,889
- Virginia Beach, VA: 450,189
- Match each of the three cities with the rounded populations in the table.
-
The table shows three ways of rounding large numbers.
- To get a rough idea of how many people are in these cities, which ways of rounding seem appropriate?
- To compare the populations or put them in order by size, which ways of rounding are more helpful? Less helpful?
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Activity Synthesis
- Select groups to share the matches they made and their reasoning.
- Display the completed table.
- Invite students to briefly share their responses to the last problem, using the table to aid their explanations.
- Point out that, in reality, it is unlikely to accurately count the exact number of people in a state. Highlight that rounding can be a useful way to get a sense of a quantity, but it requires making some decisions about what is most meaningful in a situation.
Lesson Synthesis
Lesson Synthesis
Display the completed table from a previous activity.
| round to the nearest . . . |
100,000 | 10,000 | 1,000 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 53,487 | 100,000 | 50,000 | 53,000 | 53,500 |
| 4,896 | 0 | 0 | 5,000 | 4,900 |
| 370,130 | 400,000 | 370,000 | 370,000 | 370,100 |
| 96,500 | 100,000 | 100,000 | 97,000 | 96,500 |
| 985,411 | 1,000,000 | 990,000 | 985,000 | 985,400 |
| 7,150 | 0 | 10,000 | 7,000 | 7,200 |
“What do you notice? What do you wonder?”
“Why does 370,130 round to the same number when rounded to the nearest 10,000 and 1,000?” (The nearest multiple of 1,000 and the nearest multiple of 10,000 happen to be the same number—370,000.)
“Why does 4,896 round to 0?” (It is closer to 0 than to the next closest multiple of 10,000 or of 100,000. It is more than 5,000 away from 10,000, and more than 50,000 away from 100,000.)
“Why does 985,411 round to 1,000,000 instead of a six-digit number in the hundred-thousands?” (1,000,000 is its nearest multiple of 100,000.)
Cool-down: Round Three Ways (5 minutes)
Cool-Down
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.

