Lesson 15
Distinguishing Volume and Surface Area
Let’s work with surface area and volume in context.
15.1: The Science Fair
Mai’s science teacher told her that when there is more ice touching the water in a glass, the ice melts faster. She wants to test this statement so she designs her science fair project to determine if crushed ice or ice cubes will melt faster in a drink.
She begins with two cups of warm water. In one cup, she puts a cube of ice. In a second cup, she puts crushed ice with the same volume as the cube. What is your hypothesis? Will the ice cube or crushed ice melt faster, or will they melt at the same rate? Explain your reasoning.
15.2: Revisiting the Box of Chocolates
The other day, you calculated the volume of this heart-shaped box of chocolates.
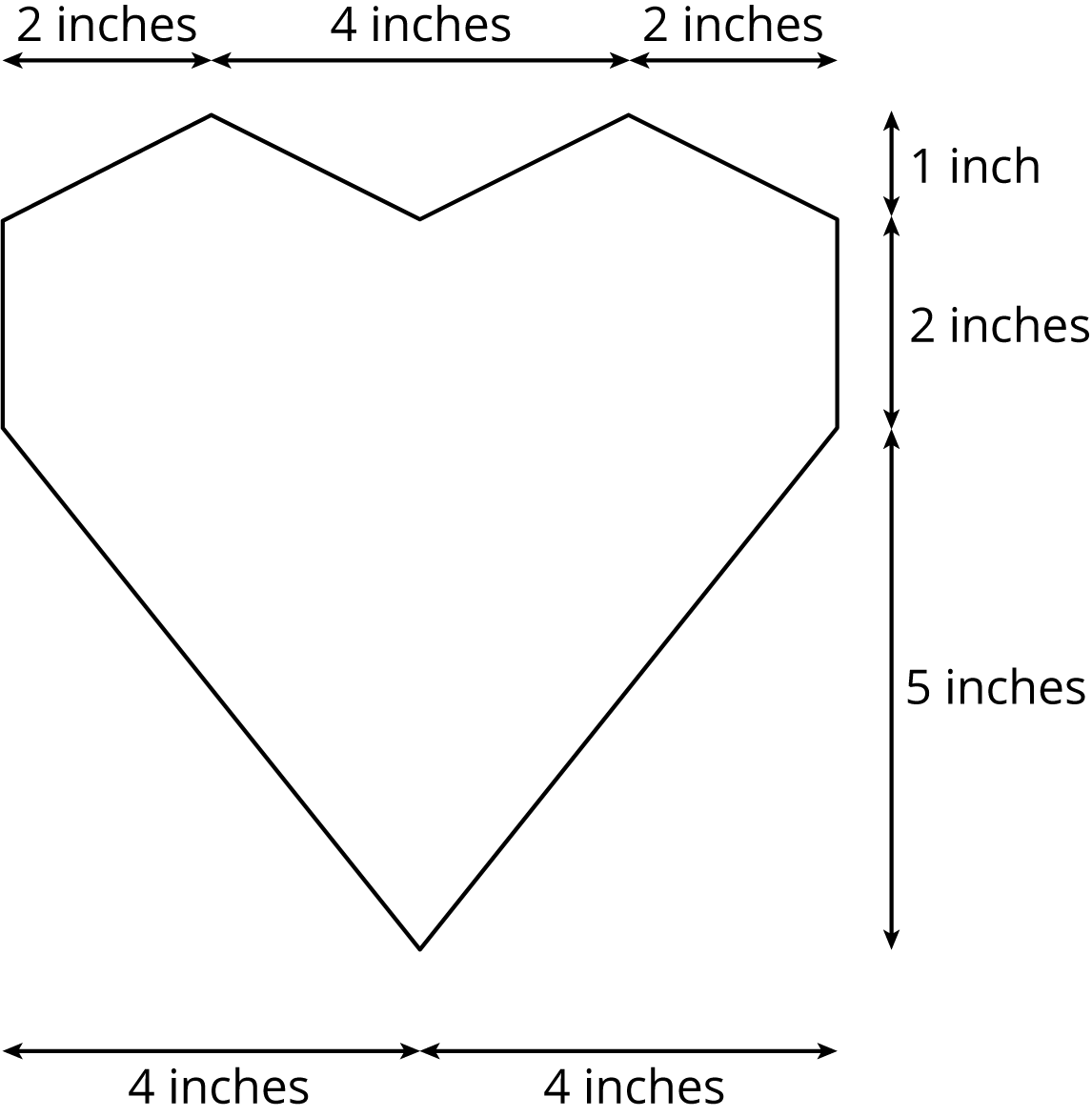
The depth of the box is 2 inches. How much cardboard is needed to create the box?
15.3: Card Sort: Surface Area or Volume
Your teacher will give you cards with different figures and questions on them.
- Sort the cards into two groups based on whether it would make more sense to think about the surface area or the volume of the figure when answering the question. Pause here so your teacher can review your work.
- Your teacher will assign you a card to examine more closely. What additional information would you need to be able to answer the question on your card?
- Estimate reasonable measurements for the figure on your card.
-
Use your estimated measurements to calculate the answer to the question.
A cake is shaped like a square prism. The top is 20 centimeters on each side, and the cake is 10 centimeters tall. It has frosting on the sides and on the top, and a single candle on the top at the exact center of the square. You have a knife and a 20-centimeter ruler.
- Find a way to cut the cake into 4 fair portions, so that all 4 portions have the same amount of cake and frosting.
- Find another way to cut the cake into 4 fair portions.
- Find a way to cut the cake into 5 fair portions.
15.4: A Wheelbarrow of Concrete
A wheelbarrow is being used to carry wet concrete. Here are its dimensions.
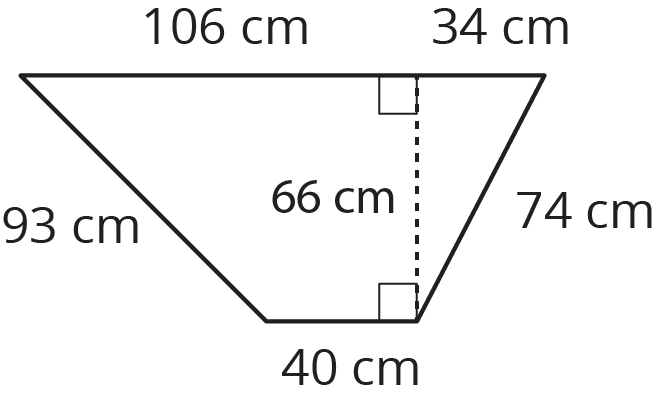
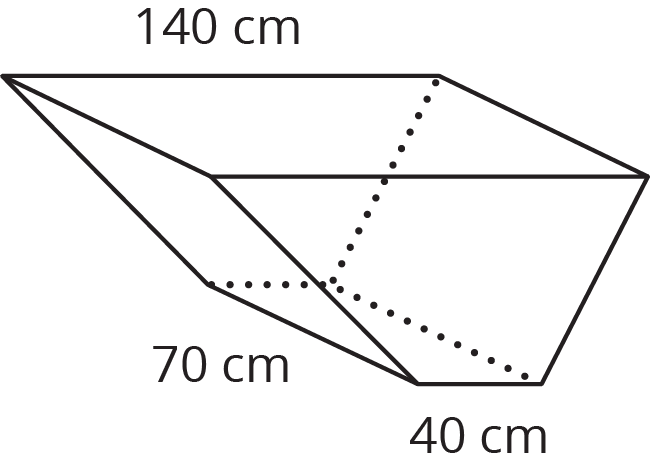
- What volume of concrete would it take to fill the tray?
-
After dumping the wet concrete, you notice that a thin film is left on the inside of the tray. What is the area of the concrete coating the tray? (Remember, there is no top.)
Summary
Sometimes we need to find the volume of a prism, and sometimes we need to find the surface area.
Here are some examples of quantities related to volume:
- How much water a container can hold
- How much material it took to build a solid object
Volume is measured in cubic units, like in3 or m3.
Here are some examples of quantities related to surface area:
- How much fabric is needed to cover a surface
- How much of an object needs to be painted
Surface area is measured in square units, like in2 or m2.
Glossary Entries
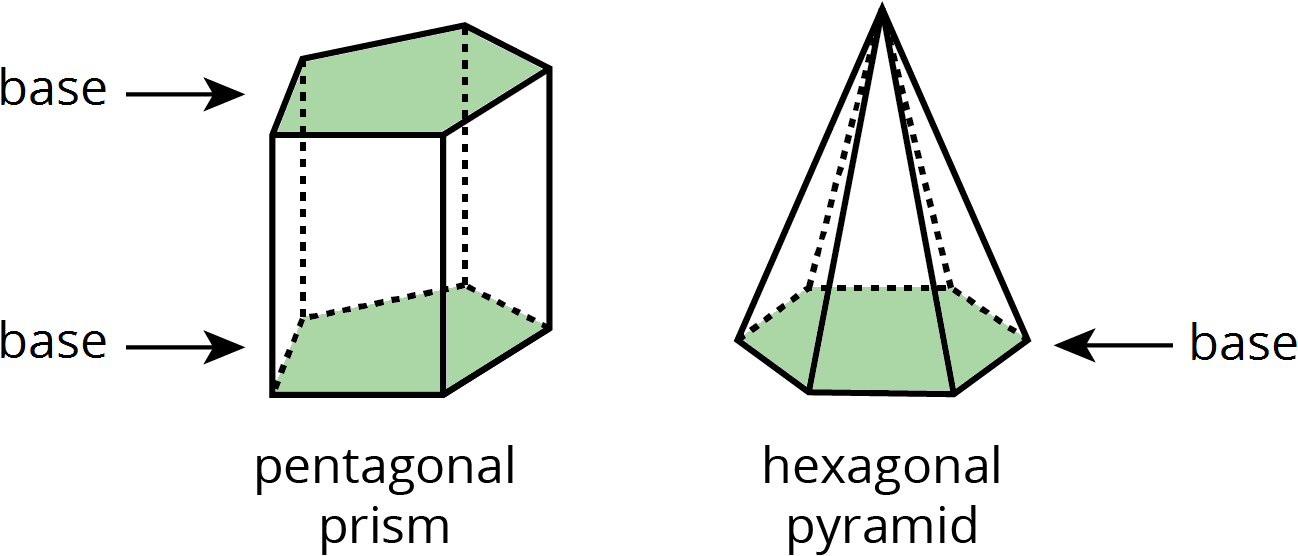
- base (of a prism or pyramid)
The word base can also refer to a face of a polyhedron.
A prism has two identical bases that are parallel. A pyramid has one base.
A prism or pyramid is named for the shape of its base.
- cross section
A cross section is the new face you see when you slice through a three-dimensional figure.
For example, if you slice a rectangular pyramid parallel to the base, you get a smaller rectangle as the cross section.
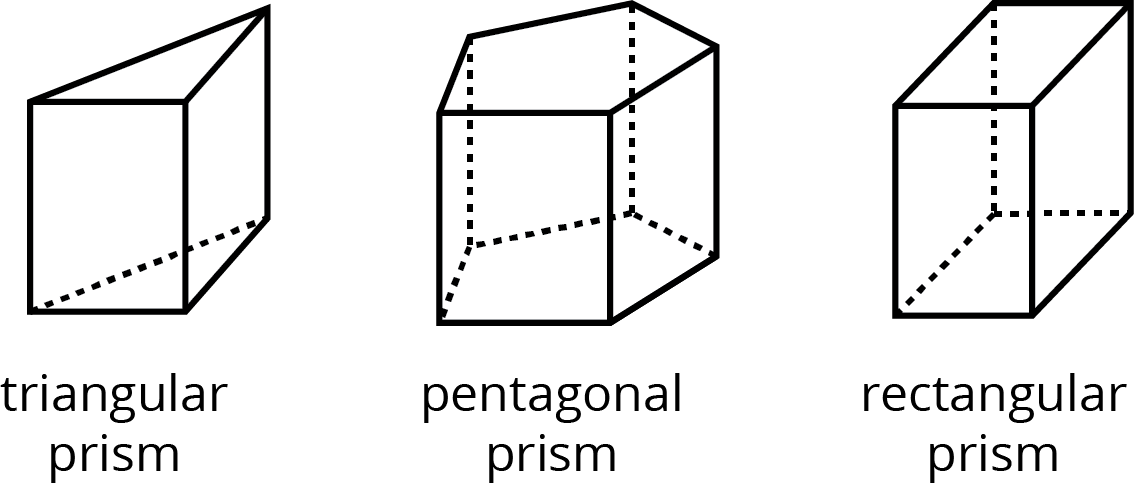
- prism
A prism is a type of polyhedron that has two bases that are identical copies of each other. The bases are connected by rectangles or parallelograms.
Here are some drawings of prisms.
- pyramid
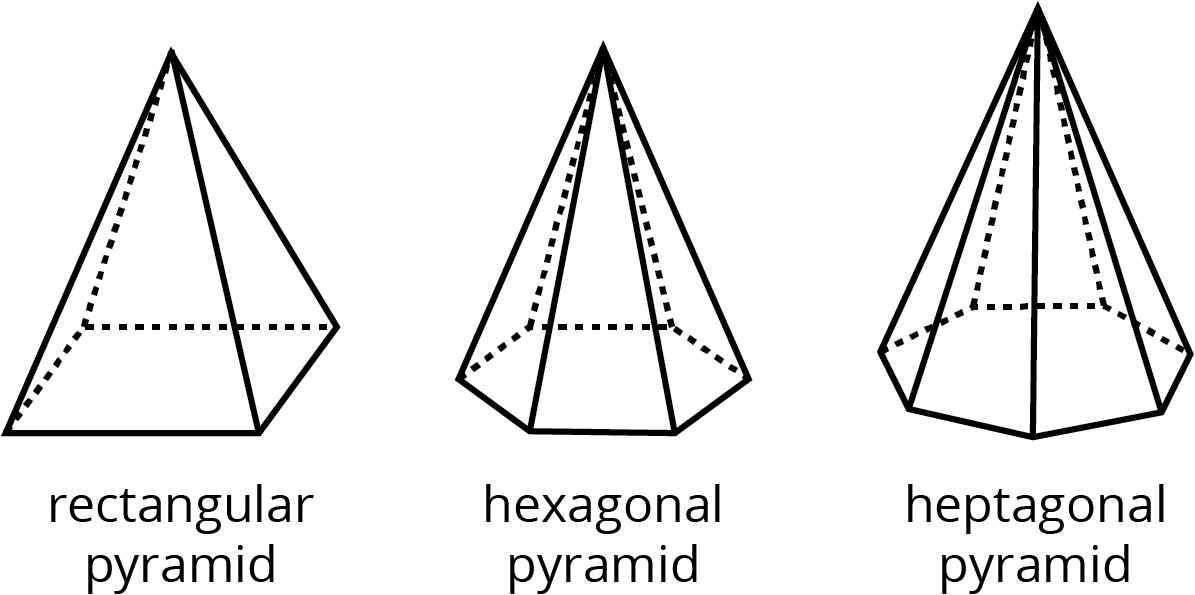
A pyramid is a type of polyhedron that has one base. All the other faces are triangles, and they all meet at a single vertex.
Here are some drawings of pyramids.
- surface area
The surface area of a polyhedron is the number of square units that covers all the faces of the polyhedron, without any gaps or overlaps.
For example, if the faces of a cube each have an area of 9 cm2, then the surface area of the cube is \(6 \boldcdot 9\), or 54 cm2.
- volume
Volume is the number of cubic units that fill a three-dimensional region, without any gaps or overlaps.
For example, the volume of this rectangular prism is 60 units3, because it is composed of 3 layers that are each 20 units3.
