Lesson 7
Exploring the Area of a Circle
Let’s investigate the areas of circles.
Problem 1
The \(x\)-axis of each graph has the diameter of a circle in meters. Label the \(y\)-axis on each graph with the appropriate measurement of a circle:
radius (m), circumference (m), or area (m2).
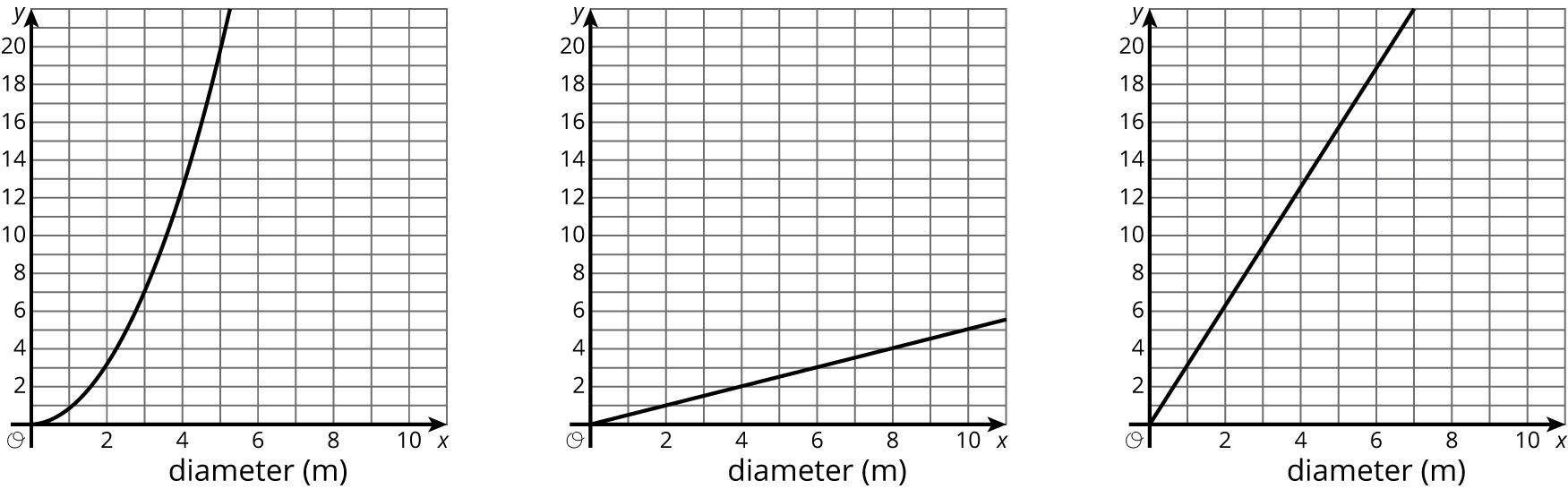
Problem 2
Circle A has area 500 in2. The diameter of circle B is three times the diameter of circle A. Estimate the area of circle B.
Problem 3
Lin’s bike travels 100 meters when her wheels rotate 55 times. What is the circumference of her wheels?
Problem 4
Priya drew a circle whose circumference is 25 cm. Clare drew a circle whose diameter is 3 times the diameter of Priya’s circle. What is the circumference of Clare’s circle?
Problem 5
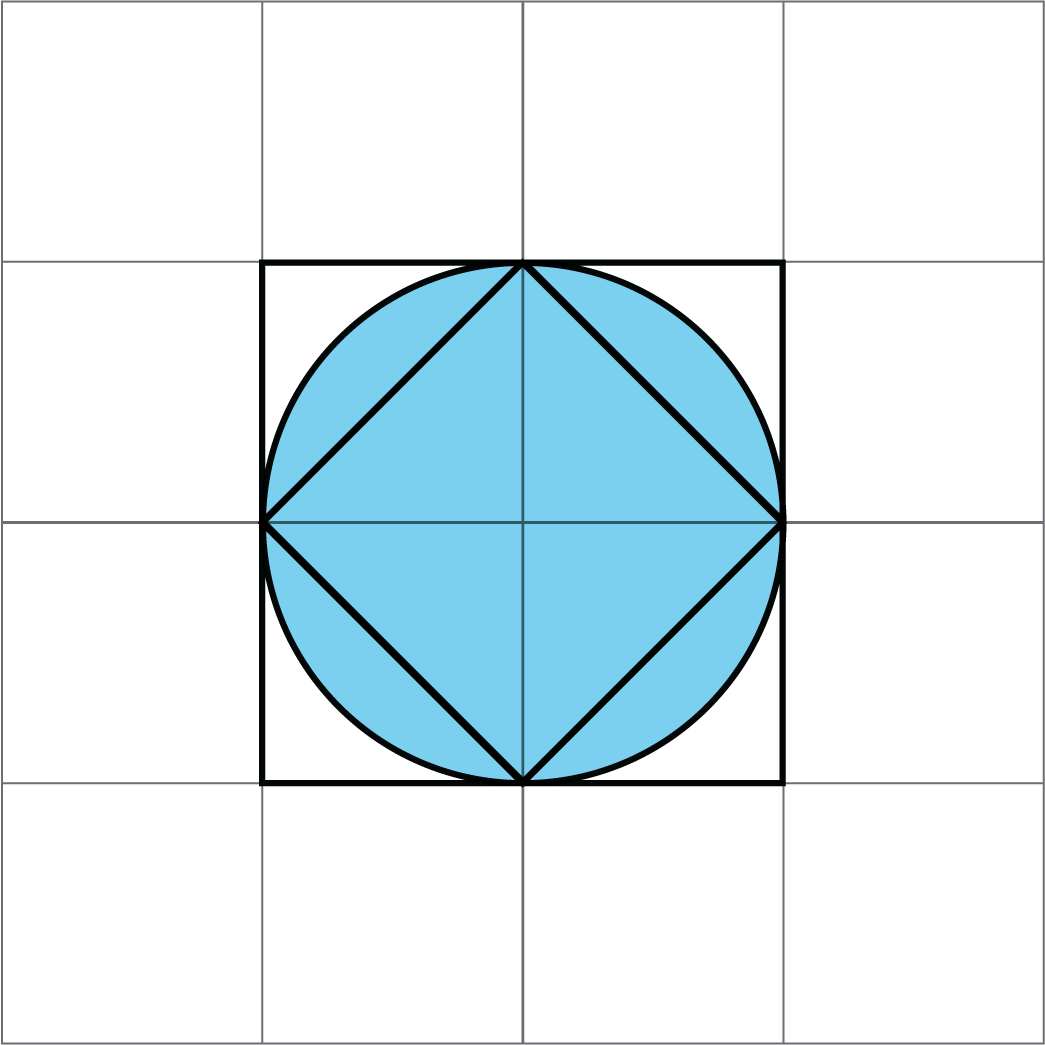
-
Here is a picture of two squares and a circle. Use the picture to explain why the area of this circle is more than 2 square units but less than 4 square units.
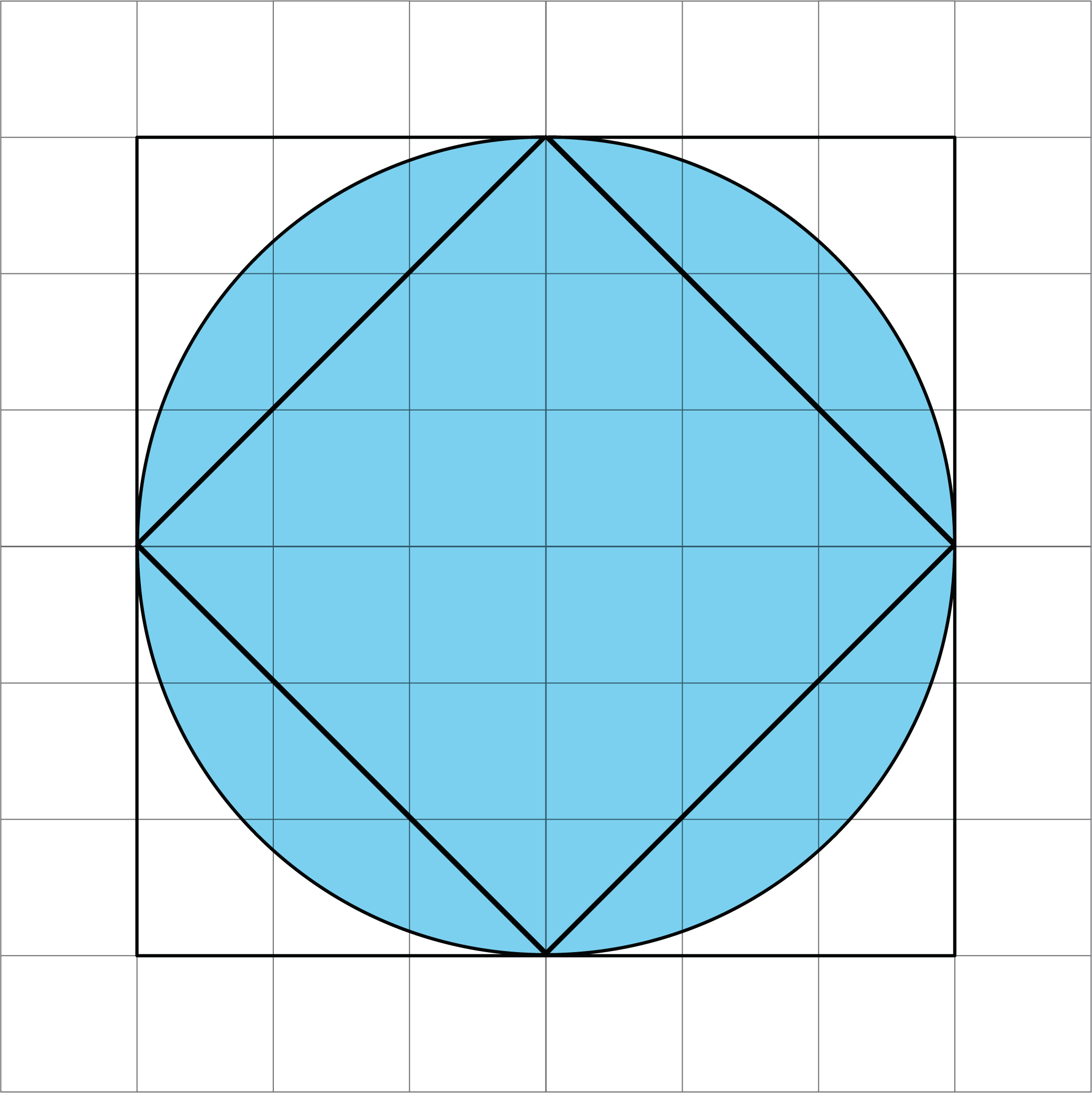
-
Here is another picture of two squares and a circle. Use the picture to explain why the area of this circle is more than 18 square units and less than 36 square units.
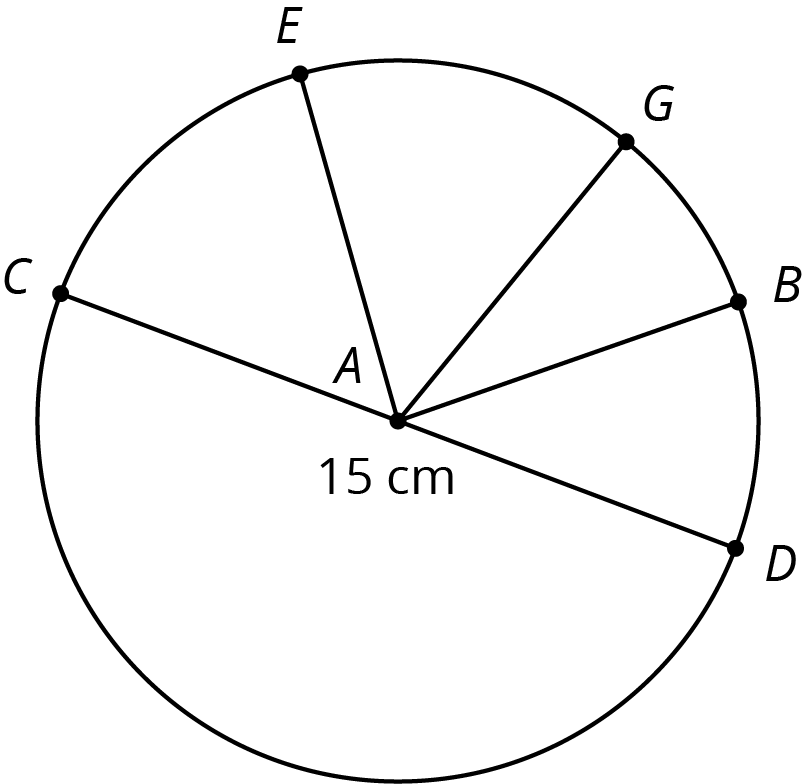
Problem 6
Point \(A\) is the center of the circle, and the length of \(CD\) is 15 centimeters. Find the circumference of this circle.