Lesson 17
Calculating Products of Decimals
17.1: Number Talk: Twenty Times a Number (5 minutes)
Warm-up
The purpose of this number talk is to have students see structure related to the distributive property in preparation for the problems using area diagrams they will solve in the lesson.
Launch
Display one problem at a time. Give students 30 seconds of quiet think time for each problem and ask them to give a signal when they have an answer and a strategy. Keep all problems displayed throughout the talk. Follow with a whole-class discussion.
Supports accessibility for: Memory; Organization
Student Facing
Evaluate mentally.
\(20 \boldcdot 5\)
\(20 \boldcdot (0.8)\)
\(20 \boldcdot (0.04)\)
\(20 \boldcdot (5.84)\)
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Activity Synthesis
Ask students to share their strategies for each problem. Record and display their responses for all to see. To involve more students in the conversation, consider asking:
- “Who can restate ___’s reasoning in a different way?”
- “Did anyone have the same strategy but would explain it differently?”
- “Did anyone solve the problem in a different way?”
- “Does anyone want to add on to _____’s strategy?”
- “Do you agree or disagree? Why?”
Design Principle(s): Optimize output (for explanation)
17.2: Using the Partial Products Method (10 minutes)
Optional activity
This activity continues using partial products and area diagrams to compute products of decimals and connect area diagrams with vertical calculations. In these problems, the side lengths and areas of the rectangle are left blank. Students fill in these fields by decomposing the factors by place value and multiplying them. Like many of the activities in this unit, the work involves understanding the structure of the base-ten system used in multiplication calculations (MP7) and making sense of it from arithmetic and geometric perspectives.
Students also make another key connection about several previously developed ideas here. They see that we can write the non-zero digits of decimal factors as whole numbers, use vertical calculations to multiply them, and then attend to the decimal point in the product afterwards. In other words, they notice the algorithm for multiplication can streamline the reasoning processes they have used up to this point.
Launch
Arrange students in groups of 2. Give groups 1–2 minutes to make sense of the first set of questions and area diagram. Listen to their discussions to make sure they understand how to label the appropriate side lengths. If needed, pause the class and have a student or a group that correctly decomposed the side lengths by place value share their reasoning.
Give students 5 minutes of quiet work time for the rest of the task. Follow with a whole-class discussion.
Student Facing
-
Label the area diagram to represent \((2.5) \boldcdot (1.2)\) and to find that product.

- Decompose each number into its base-ten units (ones, tenths, etc.) and write them in the boxes on each side of the rectangle.
- Label Regions A, B, C, and D with their areas. Show your reasoning.
- Find the product that the area diagram represents. Show your reasoning.
-
Here are two ways to calculate \((2.5) \boldcdot (1.2)\). Each number with a box gives the area of one or more regions in the area diagram.
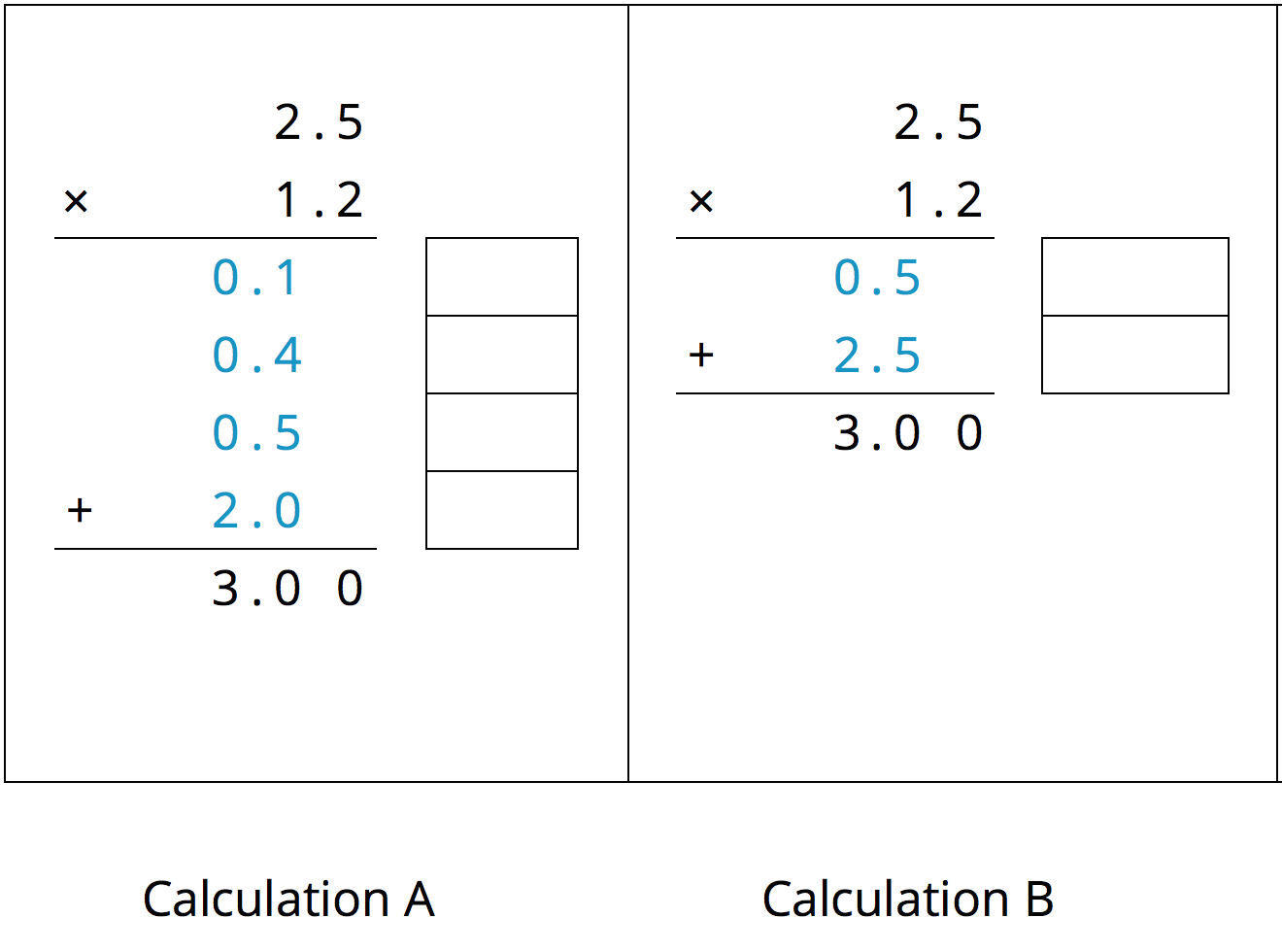
-
In the boxes next to each number, write the letter(s) of the corresponding region(s).
-
In Calculation B, which two numbers are being multiplied to obtain 0.5?
Which numbers are being multiplied to obtain 2.5?
-
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Anticipated Misconceptions
If students label side lengths with numbers that are not single-digit multiples of powers of ten, remind them to work with base-ten units as practiced in the previous lesson. Provide them with one label for a length and see if they can then find the other sections.
Activity Synthesis
Display the solution shown here for all to see.
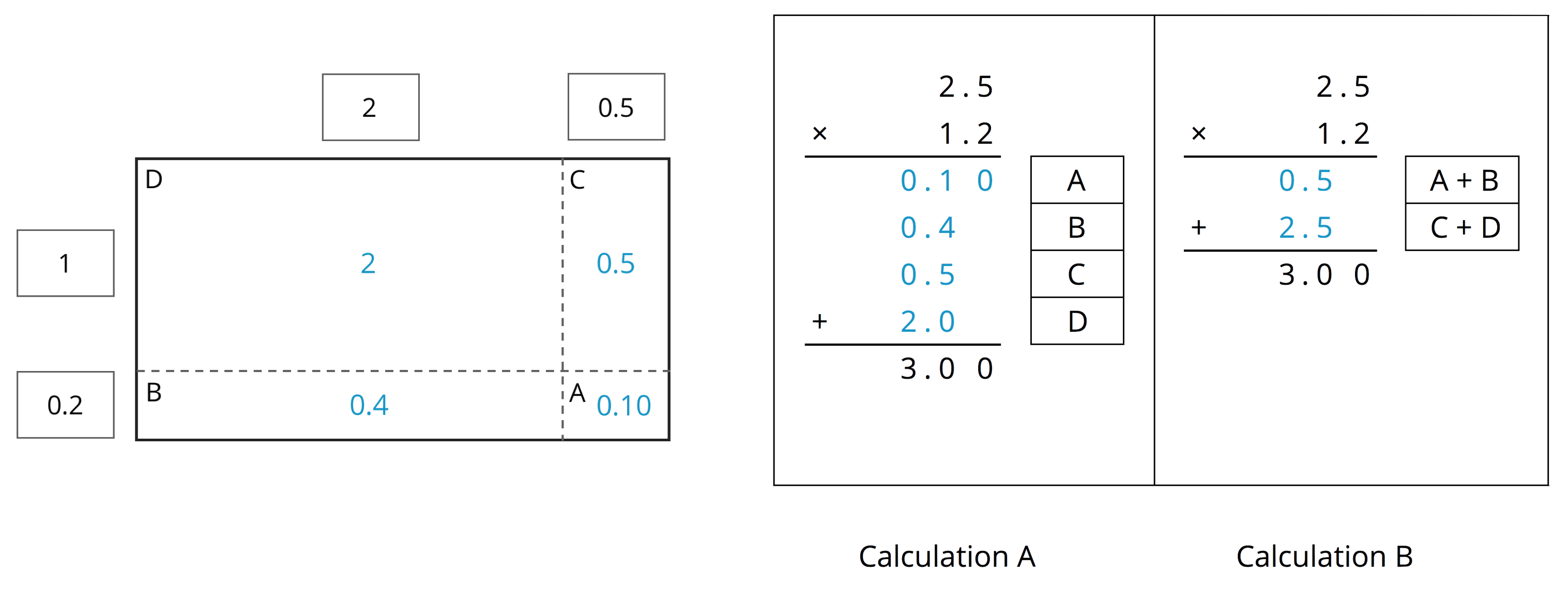
Select a few students to explain how they determined which factor belongs to which side of the rectangle and how they found each partial area. Then, ask how each blue number in the calculations, especially Calculation B, is obtained. If not mentioned in students' explanations, emphasize that the blue 0.5, represented by the area of A + B in the diagram, is the product of 0.2 and 2.5. To highlight this connection, consider shading or coloring the corresponding areas in the diagram and circling these values in the calculations. Likewise, the blue 2.5, represented by the area of C + D in the diagram, is the product of 1 and 2.5 in the calculation.
17.3: Calculating Products of Decimals (25 minutes)
Activity
Students deepen and reinforce the ideas developed in previous activities: using area diagrams to find partial products, relating these partial products to the numbers in the algorithm, and using multiplication of whole numbers to find the product of decimals. By calculating products of decimals using vertical calculations of whole numbers, students extend their understanding of multiplication to include multiplication of any pair of decimals.
Finally, with a range of methods for multiplying decimals in hand, students choose a method to solve a contextual problem. The application invites students to use MP2, deciding what mathematical operations to perform based on the context and then using the context to understand how to deal with the result of the complex calculations.
Launch
Arrange students in groups of 2. Ask students to discuss and agree on each step before moving on to the next step. Give partners 8–10 minutes to complete the first three questions and follow with a brief whole-class discussion.
Ask students to explain the first question using fractions. If not brought up by students, highlight the idea that \((2.5) \boldcdot (1.2)\) is equivalent to \(25 \boldcdot (0.1) \boldcdot 12 \boldcdot (0.1)\), which is the same as \(25 \boldcdot 12 \boldsymbol \boldcdot (0.01)\) (and also \(25 \boldcdot 12 \boldcdot \frac {1}{100}\)). The example shows that we can treat the non-zero digits of the factors as whole numbers, use the algorithm to multiply them, and then multiply the product by some power of 0.1 or \(\frac {1}{10}\) (or divide by some power of 10) and move the decimal point accordingly.
Give students 2–3 minutes of quiet work time on the last question. Follow with a whole-class discussion.
Supports accessibility for: Memory; Conceptual processing
Design Principle(s): Optimize output; Maximize meta-awareness
Student Facing
-
A common way to find a product of decimals is to calculate a product of whole numbers, then place the decimal point in the product.
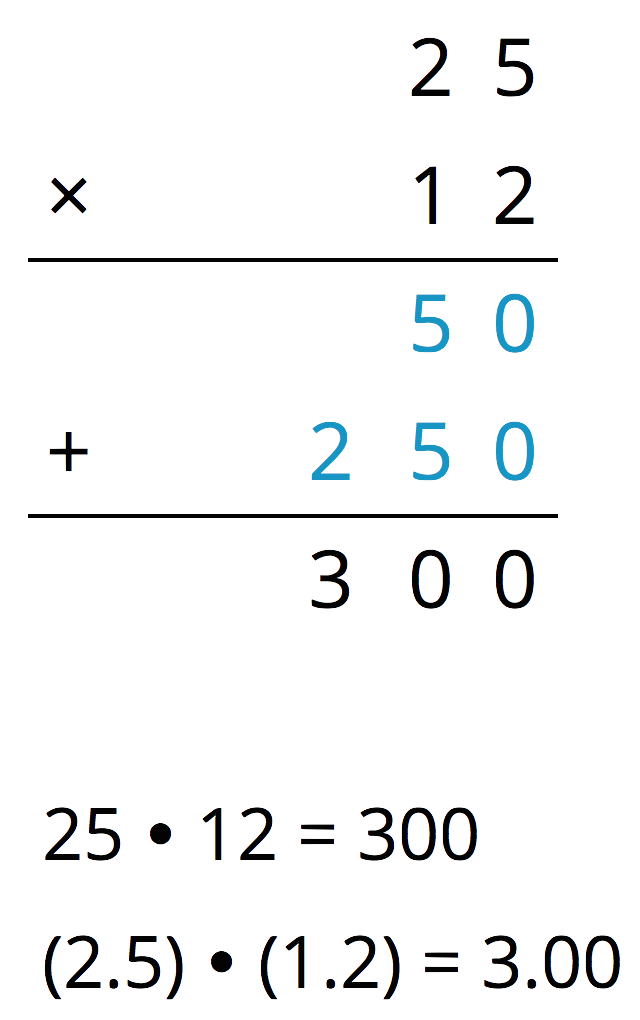
Here is an example for \((2.5) \boldcdot (1.2)\).
Use what you know about decimals and place value to explain why the decimal point of the product is placed where it is.
-
Use the method shown in the first question to calculate each product.
- \((4.6) \boldcdot (0.9)\)
- \((16.5) \boldcdot (0.7)\)
-
Use area diagrams to check your earlier calculations. For each problem:
- Decompose each number into its base-ten units and write them in the boxes on each side of the rectangle.
- Write the area of each lettered region in the diagram. Then find the area of the entire rectangle. Show your reasoning.
-
\((4.6) \boldcdot (0.9)\)

-
\((16.5) \boldcdot (0.7)\)

-
About how many centimeters are in 6.25 inches if 1 inch is about 2.5 centimeters? Show your reasoning.
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Anticipated Misconceptions
Students may not recall how to use the algorithm to multiply whole numbers. Consider reviewing the process prior to the activity.
Students may think that when calculating products, the decimal points need to line up. They may even write extra zeros at the end of a factor so there are the same amount of decimal places in each factor. Although this will not affect the answer, it is more efficient to align both factors to the right. If extra zeros are written at the end of a factor, there will be extra zeros accumulated in the calculation, and this can lead to careless errors.
Activity Synthesis
Most of the discussions will have occurred in groups, but debrief as a class to tie a few ideas together. Ask a few students to share how they vertically calculated the products in the last several questions or to display the solutions for all to see. Discuss questions like:
- How did you know how to label the lengths of A, B, and C on the 16.5 by 0.7 rectangle? (The three digits in the number represent 10, 6, and 0.5, so the longest side is 10, the medium-length side is 6, and the shortest side is 0.5.)
- Which method—drawing an area diagram or using vertical calculations—do you prefer in finding products such as \((16.5) \boldcdot (0.7)\)? Why? (Drawing an area diagram, because the visual representation helps us break up the calculation into smaller, more manageable pieces: \(10 \boldcdot (0.7)\), \(6 \boldcdot (0.7)\), and \((0.5) \boldcdot (0.7)\). Vertical calculation, because it is quicker to just multiply whole numbers and move the decimal point.)
- How did you know where to place the decimals in the last problem? (For part a, since 4.6 is 46 tenths and 0.9 is 9 tenths, we can compute \(46 \boldcdot 9\) and then multiply the product by \((\frac{1}{10} \boldcdot \frac{1}{10})\) or by \(\frac{1}{100}\) to find \((4.6) \boldcdot (0.9)\).)
17.4: Practicing Multiplication of Decimals (15 minutes)
Optional activity
This optional activity is an opportunity to practice the methods in this lesson to calculate products of decimals, and students have an opportunity to practice multiplying decimals in a real-world context. Students can choose to use area diagrams to help organize their work and support their reasoning. However, the goal of the activity is to have students practice using the multiplication algorithm on decimals.
Launch
Give students quiet think time to complete the activity and then time to share their explanation with a partner. Follow with whole-class discussion.
Supports accessibility for: Visual-spatial processing; Organization
Student Facing
-
Calculate each product. Show your reasoning. If you get stuck, consider drawing an area diagram to help.
-
\((5.6) \boldcdot (1.8)\)
-
\((0.008) \boldcdot (7.2)\)
-
-
A rectangular playground is 18.2 meters by 12.75 meters.
- Find its area in square meters. Show your reasoning.
- If 1 meter is approximately 3.28 feet, what are the approximate side lengths of the playground in feet? Show your reasoning.
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Student Facing
Are you ready for more?
-
Write the following expressions as decimals.
- \(1-0.1\)
- \(1-0.1+10-0.01\)
- \(1-0.1+10-0.01+100-0.001\)
- Describe the decimal that results as this process continues.
- What would happen to the decimal if all of the addition and subtraction symbols became multiplication symbols? Explain your reasoning.
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Activity Synthesis
Select students to share their strategies, being sure to highlight approaches using area diagrams and vertical calculations. Record the representations or strategies students share and display them for all to see.
Design Principle(s): Support sense-making; Cultivate conversation
Lesson Synthesis
Lesson Synthesis
We have learned several ways to calculate products of decimals—by using fractions, multiplying non-zero digits of the decimals, using area diagrams and finding partial products, and calculating vertically.
- How can working in fraction form help us find the product of two decimals?
- How can the product of two whole numbers (e.g., 48 and 19) help us find the product of two decimals with the same digits (e.g., 0.048 and 1.9)?
- How can we decompose decimal factors so they can be multiplied efficiently?
17.5: Cool-down - Calculate This! (5 minutes)
Cool-Down
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners.
Student Lesson Summary
Student Facing
Suppose that we want to calculate the product of two numbers that are written in base ten. To explain how, we can use what we know about base-ten numbers and areas of rectangles.
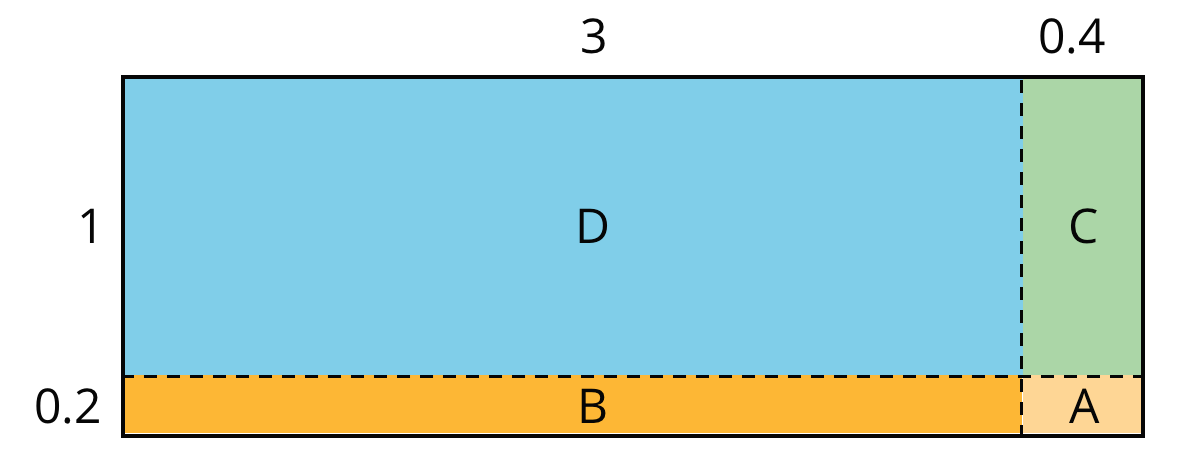
Here is a diagram of a rectangle with side lengths 3.4 units and 1.2 units.
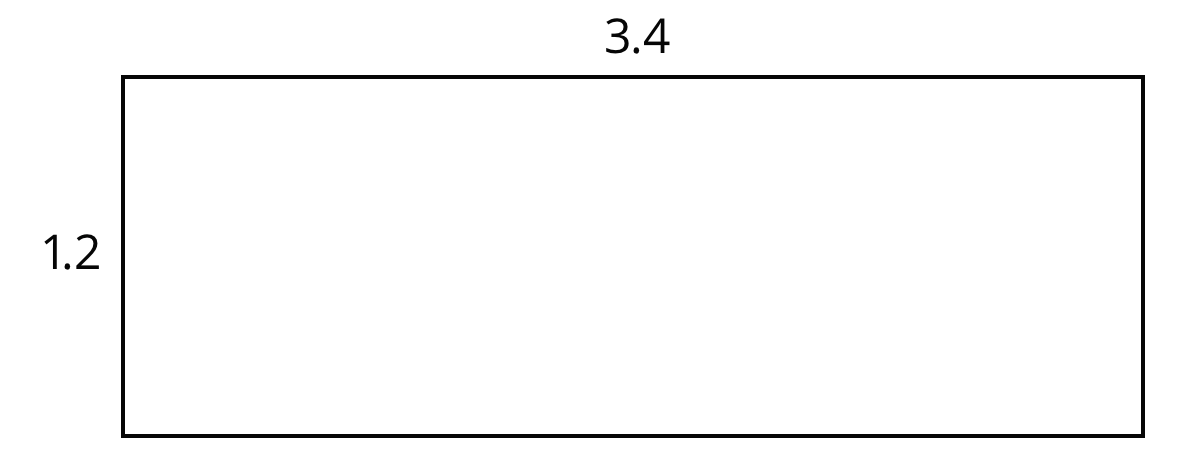
Its area, in square units, is the product
\((3.4) \boldcdot (1.2)\)
To calculate this product and find the area of the rectangle, we can decompose each side length into its base-ten units, \(3.4 = 3 + 0.4\) and \(1.2= 1 + 0.2\), decomposing the rectangle into four smaller sub-rectangles.
We can rewrite the product and expand it twice:
\(\begin{align} (3.4) \boldcdot (1.2) &= (3 + 0.4) \boldcdot (1 + 0.2)\\ &=(3 + 0.4) \boldcdot 1 + (3 + 0.4) \boldcdot 0.2\\ &=3 \boldcdot 1+ 3 \boldcdot (0.2)+ (0.4) \boldcdot 1 + (0.4)\boldcdot (0.2)\\ \end{align}\)
In the last expression, each of the four terms is called a partial product. Each partial product gives the area of a sub-rectangle in the diagram. The sum of the four partial products gives the area of the entire rectangle.
We can show the horizontal calculations above as two vertical calculations.
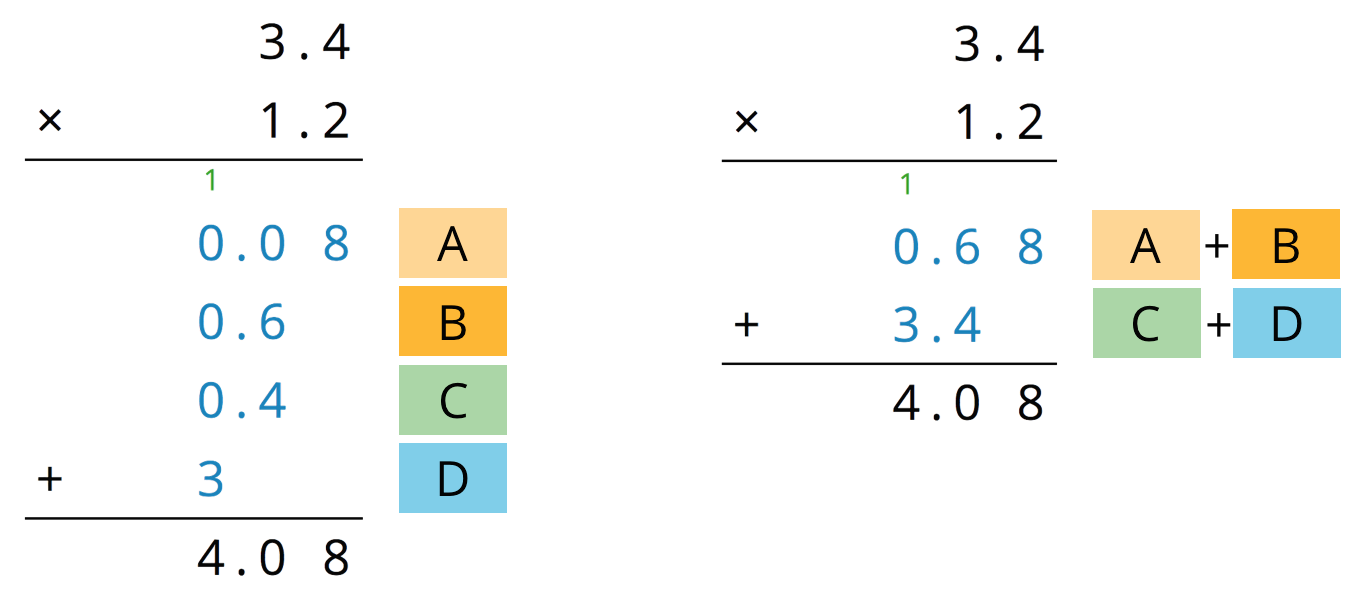
The calculation on the left is an example of the partial products method. It shows the values of each partial product and the letter of the corresponding sub-rectangle. Each partial product gives an area:
- A is 0.2 unit by 0.4 unit, so its area is 0.08 square unit.
- B is 3 unit by 0.2 unit, so its area is 0.6 square unit.
- C is 0.4 unit by 1 unit, so its area is 0.4 square unit.
- D is 3 units by 1 unit, so its area is 3 square units.
- The sum of the partial products is \(0.08 + 0.6 +0.4+ 3\), so the area of the rectangle is 4.08 square units.
The calculation on the right shows the values of two products. Each value gives a combined area of two sub-rectangles:
- The combined regions of A and B have an area of 0.68 square units; 0.68 is the value of \((3 + 0.4) \boldcdot 0.2\).
- The combined regions of C and D have an area of 3.4 square units; 3.4 is the value of \((3 + 0.4) \boldcdot 1\).
- The sum of the values of two products is \(0.68 + 3.4\), so the area of the rectangle is 4.08 square units.