Lesson 16
How Many Solutions?
Let’s solve equations with different numbers of solutions.
Problem 1
Lin was looking at the equation \(2x-32+4(3x-2462) = 14x\). She said, “I can tell right away there are no solutions, because on the left side, you will have \(2x+12x\) and a bunch of constants, but you have just \(14x\) on the right side.” Do you agree with Lin? Explain your reasoning.
Problem 2
Han was looking at the equation \(6x-4+2(5x+2)=16x\). He said, “I can tell right away there are no solutions, because on the left side, you will have \(6x+10x\) and a bunch of constants, but you have just \(16x\) on the right side.” Do you agree with Han? Explain your reasoning.
Problem 3
Decide whether each equation is true for all, one, or no values of \(x\).
- \(6x-4=\text-4+6x\)
- \(4x-6=4x+3\)
- \(\text-2x+4=\text-3x+4\)
Problem 4
Solve each of these equations. Explain or show your reasoning.
-
\(3(x-5) = 6\)
-
\(2\left(x - \frac{2}{3}\right) = 0\)
-
\(4x - 5 = 2 -x\)
Problem 5
In the picture triangle \(A’B’C’\) is an image of triangle \(ABC\) after a rotation. The center of rotation is \(E\).
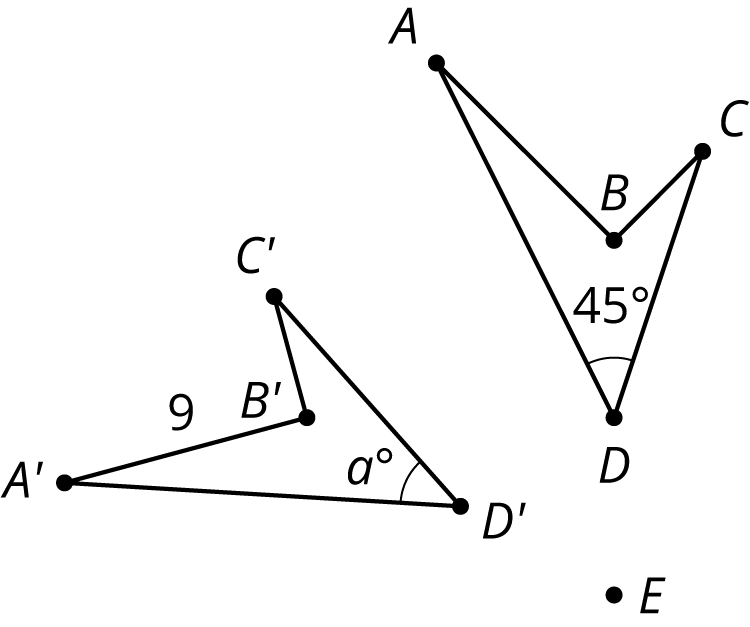
- What is the length of side \(AB\)? Explain how you know.
- What is the measure of angle \(D'\)? Explain how you know.
Problem 6
Solve each of these equations. Explain or show your reasoning.
\(2(x+5)=3x+1\)
\(3y-4=6-2y\)
\(3(n+2)=9(6-n)\)